NURS FPX 4015 Assessment 3 Sample FREE DOWNLOAD
NURS FPX 4015 Assessment 3 Concept Map: The 3Ps and Mental Health Care
Student Name
Capella University
NURS-FPX4015 Pathophysiology, Pharmacology, and Physical Assessment: A Holistic Approach to Patient-Centered Care
Professor Name
Date
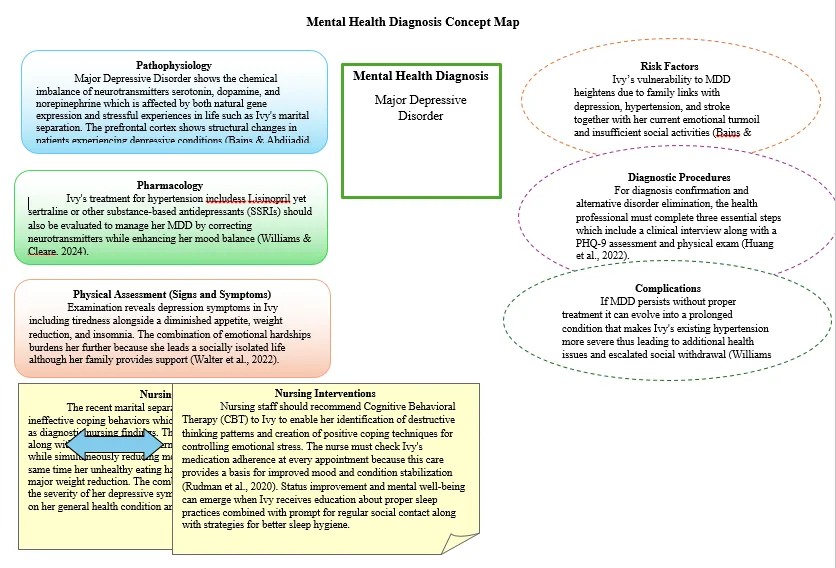
Mental Health Diagnosis Concept Map
Instructions To Write NURS FPX 4015 Assessment 3
If you need guidance to write NURS FPX 4015 Assessment 3 Concept Map: The 3Ps and Mental Health Care, contact Tutors Academy. Our expert tutors are ready to help you succeed.
Instruction file for 4015 Assessment 3
Contact us to get the instruction file for this assessment.
Scoring Guide for 4015 Assessment 3
Contact us to get the Scoring file for this assessment.
A List Of Capella Library References
Huang, X.-J., Ma, H.-Y., Wang, X.-M., Zhong, J., Sheng, D.-F., & Xu, M.-Z. (2022). Equating the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 to the HADS depression and anxiety subscales in patients with major depressive disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 311, 327–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2022.05.079
Walter, H. J., Abright, A. R., Bukstein, O. G., Diamond, J., Keable, H., Ripperger-Suhler, J., & Rockhill, C. (2022). Clinical practice guideline for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with major and persistent depressive disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 62(5), 479–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2022.10.001
Rudman, A., Arborelius, L., Dahlgren, A., Finnes, A., & Gustavsson, P. (2020). Consequences of early career nurse burnout: A prospective long-term follow-up on cognitive functions, depressive symptoms, and insomnia. EClinicalMedicine, 27(100565). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100565
Williams, R., & Cleare, A. (2024). Drug and physical treatment of depression. In Seminars in General Adult Psychiatry. https://books.google.com.pk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=ATcAEQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA108&dq=prescribed+Lisinopril+for+hypertension%3B+however
Bains, N., & Abdijadid, S. (2020, July 10). Major depressive disorder. Europepmc.org. https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk559078
Related Free Sample for NURS-FPX4015
Best Professors To Choose From For 4015 Class
- Marissa Grimley, DNP, RN, PHN
- Yvonne Bell, MBA, MSN, BSN
- Heinz Bartnick, DNP, MSN, BSN, AS
- Mary Ann Anderson, PhD, MS, BSN
- James White, DNP, MSN, BSN
(FAQs) related to NURS FPX 4015 Assessment 3
Question 1: From where can I download a free sample for NURS FPX 4015 Assessment 3?
Answer 1: You can download a free sample for NURS FPX 4015 Assessment 3 from the Tutors Academy website.
Question 2: Where can I find the instructions and rubric file for NURS FPX 4015 Assessment 3?
Answer 2: You can find the rubric and instruction files for this assessment on the Tutors Academy sample page for NURS FPX 4015 Assessment 3.
Do you need a tutor to help with this paper for you with in 24 hours.
- 0% Plagiarised
- 0% AI
- Distinguish grades guarantee
- 24 hour delivery

