
BHA FPX 4020 Assessment 3
Data Collection and Analysis
Security breaches are one of the biggest dangers concerning the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information in healthcare organizations such as Emory University Medical Center (EUMC). Data gathering and processing are crucial in managing all these breaches because they are fundamental to comprehending the problem in its entirety (Koopmans & Mouter, 2020).
As the objective of this evaluation is to establish the weaknesses that exist in the way EUMC collects and analyses data regarding data breaches it is crucial that the assessment focuses on the following areas. Analyzing the current practices and suggesting the positive aspects and the flaws as well as the opportunities for their changes will allow the assessment of the effectiveness of EUMC’s measures towards the timely detection and efficient response and prevention of data breaches. Conducted at EUMC, the goal of this evaluation is to prevent data risks and shield the patient data, with the goal of attaining compliance.
Rationale for Cost Benefit Analysis Tool
When it comes to decision making in tackling the issue of data breaches relating to the delivery of healthcare with the aid of technology, the most suited problem analysis tool is the CBA if given the particular problem of breaches at Emory University Medical Center. The advantage of using CBA is based on offering a step-by-step assessment of the financial impacts of the intended actions (Koopmans & Mouter, 2020).
Due to CBA’s structured approach of examining the various cost/benefit repercussions linked to possible solutions, this strategy can effectively assist stakeholders in the management of their resources and investments. This aids to focus on activities that will have the most impact towards changing the organization and this will aid the process of decision making and resource allocation.
Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) is connected to the problem of data breaches at Emory University Medical Center in the sense that it presents a system and methodological tool to evaluate the impact of the problem in questions at financial level (Mouter et al. , 2020). It assist in placing dollar values on the liabilities arising from data breaches in terms of fines, legal expenses as well as compare them to the possibilities of adding security measures which though assisting organizations in deciding where to devote resources in order to minimize risks and enhance on data protection.
CBA is one of the most popular tools used in healthcare management since it aims at showing a clear structure in instances of effective cost evaluation for probable intercessions. As a result, CBA may provide a logical framework for comparing the costs and benefits of potential solutions to the problems that organisations’ managers face while managing shortage of funds and competing priorities in healthcare organisations (Biancardo et al. , 2022).
This way CBA structures both tangible and intangible values, for instance, costs and financial returns, time saving or production, patients’ quality of life improvement, and organizational efficiencies to assist the decision makers in allocation and investment decision making. Further, CBA enables comparing the various possible options of action that are available, which assists in prioritizing projects based on the greatest net benefit to the organization (Biancardo et al. , 2022).
Taking this into consideration, it is possible to identify the following reasons for choosing CBA to analyze the specified healthcare problem: depending on the techniques and tools that have been identified in the course of the study, it is possible to provide an adequate and objective overview of potential costs and benefits related to the analysis of the given problem and the subsequent development of the most suitable solutions and strategies.
Analyzing Data Relative to Internal and External Benchmarks
Among considerations in evaluating data loss at Emory University Medical Center as well as discussing the prospects for minimization, there is a critical step of comparing figures with internal and external references. Organizations end up using internal benchmarks because they are specific to the company; thus, it is possible to compare the current performance to previous performance or other predetermined parameters (Algarni et al. , 2021).
The suggested performance standard concerning the mitigation of data breaches is the use of industry security best practices, with a goal of achieving at least a 50% reduction in breaches within six months, according to the experts (Algarni et al. , 2021). For instance, if in the past EUMC was facing in average 10 data breaches per year the internal benchmark of measures to achieve could be 50% less in six months.
However, in the light of data available in A2 with regards to breach reduction attempts by EUMC, it is evident that the firm has been only able to reduce the breach level up to 30% therefore creating the impression of a performance inequality when compared against internal benchmarks (Algarni et al. , 2021).
The internal benchmark highlights the need to strengthen measures of data protection as a way of combating these vices, so as to protect the patient information as well as the organizational integrity. For this reason, EUMC can use the internal benchmark to monitor the progress in the accomplishment of goals on the reduction of data breaches as well as the general improvement of data security (Campbell et al. , 2023).
On the other hand, External Controls serve to offer more general information about the performance by comparing to the designated industry standards or other well-known models.
The external benchmark that will be applied for EUMC is the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Security Rule. The reason for selecting this external benchmark is based on the fact that the organization has been seeking to achieve national accreditation seeking to protect patients’ PHI.
The safeguarding of patient’s information under HIPAA should be a mandatory aspect of any healthcare facility due to the legal sanctions that come with HIPAA noncompliance (Dagher et al. , 2019). Thus, when compliance standards are integrated with data security practices, the EUMC has a better chance to protect sensitive information, increase patients’.
The HIPAA Security Rule has set mechanism that provides vast rules to protect the PHI and these rules include the Administrative, Physical, and Technical rules. Staying with these requirements helps to meet legal and regulatory practices and also minimize risk to patient data and general patient confidence.
Also, compliance with HIPAA standards enhances the healthcare entities’ data sharing and interoperability, which is crucial for efficient and unified patient care (Kush et al. , 2020). Hence, there is a necessity for EUMC to ensure that their data security enforcement meets HIPAA policies to ensure that patient information is protected as required by the law and to minimize on the possibility of a break-in as much as possible.
When comparing Emory University Medical Center’s data breaches with other similar organizations, competitors, or the Insurance industry, external reference standards consist of Industry standards and benchmarks constitute the external references selected for use in assessment.
Such standards can provide Emory with concepts on how its competitors and counterparts manage their data and protect them, thus helping Emory to evaluate its performance, recognize shortcomings, and its policies and procedures in a manner most effective to ensure the augmentation of data security throughout the health care organization.

Evidence-Based Recommendations for Addressing Data Breaches
Cybersecurity threats remain one of the formidable threats affecting the healthcare industry because they compromise patient identity and the institution’s credibility (Seh et al. , 2020).
These recommendations, which are based on analyzing the available sources of knowledge, deals with this multifaceted problem by analyzing the recommendations originating from authoritative sources on cybersecurity, legal and regulatory requirements, and organizational practices.
Observance of Other Conventional Security Measures
The best security features that cybersecurity experts encourage to be put in place at Emory University Medical Center (EUMC) consist of encryption, access control and intrusion detection systems.
These protocols are critical in protecting patients’ data and mitigating access by individuals who are not proficient in the handling of these data (Stewart, 2022). If EUMC follows the mentioned recommendations, it will be possible to strengthen its data protection and security, increase the protection of patients’ rights, and reduce threats to the information systems of the institution.
Monitor IT Infrastructure Continuously and Escalate All The Incidents
It is possible to state that the proper system of network activity monitoring and its incident response is crucial for EUMC’s functioning. EUMC needs to enhance the technological possibilities of monitoring and create detailed concepts of response to extreme events.
BHA FPX 4020 Assessment 3 Data Collection and Analysis
As noted, this measures allows early identification and control of data breaches and their detrimental effects on patients’ confidentiality and organization’s functioning. When security incidents are addressed in the shortest time possible, EUMC can effectively respond to security issues and continue to improve on the protection of patients’ data and ensure the public and patients’ confidence in the organization.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
In order to avoid penalties and to protect the patient’s data, Emory University Medical Center (EUMC) has to strictly follow the legal requirements like HIPAA and GDPR that are in force for protection of patients’ information. EUMC must therefore be assessing the organization’s compliance with data security standards on a regular basis , carry out self – assessments, and ensure that their staff is frequently trained in the observance of these standards (D’Arcy et al. , 2020).
The following regulations are always important to follow in EUMC so as to ensure patient’s privacy is respected, sensitive information is safeguarded from other people and the danger of leakage reduced: Keeping legal compliance also helps retain patient confidence in receiving care from EUMC while also depicting the organization’s consideration of legal and ethical guidelines in dealing with overall sensitive information regarding health care.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Data Breaches Prevention Strategies
The selected elements of the analysis tool called Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) are pivotal to determining the approach to data breaches at Emory as they enable the identification of both direct monetary costs and broader benefits associated with risks to patients’ data, utilizing estimations of cost and quantification of benefit among CBA’s major components (Biancardo et al. , 2022).
Costs directly associated with data protection and breach prevention include the expenses on security technologies and systems, personnel education, compliance with legal requirements, development of crisis response measures, possible legal expenses, reputation loses which might occur in the form of reduced customers’ trust or material losses because of business interruption, and time lost due to cyber threats (Kampová et al. , 2020).
Management expenses include the determination of resources to be used in cybersecurity awareness, campaigns, seminars, and exercises. The above interventions seeks to increase the personnel’s awareness and competence in matters concerning data security in an attempt to discouraging and/or prevent the occurrence of security breaches stemming from people’s mistakes.
It is indicated that the importance influence of data breaches in the US is highly economical and its approximate amount ranges from $3. 86 million to $8. 64 million per breach. In addition, the annual cost of cybercrime in United States of America was projected to go above $1.
Approximately 5$ trillion, which underlines the impressive proportion of the economic consequences for companies and the global economy as a whole (Unger, 2021). Introduced security measures are based on industry best practices and their application costs are in the range of $200,000-$900,000. A 20% reduction in these breaches could possibly mean a yearly savings of $3 million by preventing the need for treatments and additional days’ stay.
In this context, the costs of continuous monitoring and the introduction of measures for incident response require initial investments to acquire better monitoring systems, with the estimate varying between $ 300 000 to $ 1. Of great importance is the estimation of receivables since it has a direct impact on the amount of money the business will accept on credit sales, as calculated by Zhang et al. , (2022).
Adherence to laws and specific regulatory requirements such as HIPAA and GDPR require the first one-off expenses for auditing procedures, staff awareness, and system updates, and going by the reports the implementation costs of these are likely to range between $150,000 and $500,000 (Koopmans & Mouter, 2020). However, sustaining compliance results in vast potential saving which for organizations result to penalties of up to $1.
HIPAA violations are penalized to the tune of $ 5 million per incidence. The process of introducing data encryption and access controls entails, at first, the costs of the licences $100,000 – $300,000 of software and additional equipment, and briefing of the personnel.
However, the potential cost savings are massive as there is a possibility that hackers can limit an organization’s financial profits after a data breach to a measly $3. 86 million per incident as Saleem and Naveed stated (2020). Providing strong protection has a direct relation with business risk mitigation, and it stops harm to data and prevents major financial loss.
| Interventions | Implementation Costs | Potential Cost Savings |
| Industry-Standard Security Protocols | $200,000 – $900,000 | $3 million |
| Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response | $300,000 – $1.2 million | Up to $4 million annually |
| Compliance with Regulatory Standards | $150,000 – $500,000 | Penalties up to $1.5 million |
| Data Encryption and Access Controls | $100,000 – $300,000 | $3.86 million per incident |
| Cybersecurity Awareness Training | $50 – $200 per employee | $3.88 million per incident |
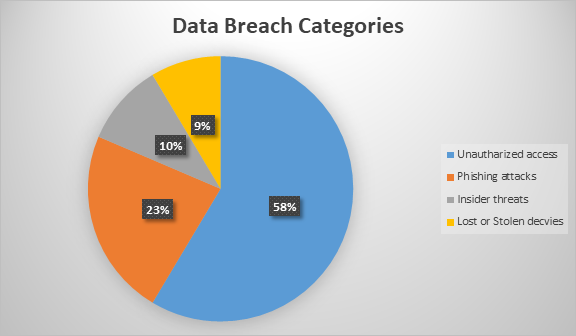
The pie chart shows the percentage of data breach categories in Emory University Medical Center (EUMC). Of all the breaches, 58% are due to unauthorized access indicating poor implementation of access controls or user authentication.
Unsophisticated as these attacks may sound, pdf phishing attacks alone are ranked as 23% of breaches, meaning that social engineering continues to pose a major threat to security. An insider threat is defined as attacks within organizations and are only responsible for 10% of the breaches which involves a person with valid credentials within the organization.
Also, stolen or lost devices are attributed to 9% of breaches underlining the significance of keeping devices safe and utilizing appropriate encryption (Roumani, 2022). Knowledge of these categories is necessary for EUMC to identify the priority areas for cybersecurity measures, as well as to prevent threats susceptible to targeted prevention measures, and thus strengthen security against the above threats as well as protecting patient data and the organization’s integrity.
Scholarly Justification for Recommendations
The suggestions made to Emory University Medical Center (EUMC) are derived from academic literature and current practices in dealing with the issues related to data breaches in healthcare organizations. To understand this further, every recommendation is unique because they deliver different forms of values that enhance the existing data security situation at EUMC and the protection of patients’ information (Stewart, 2022).
Cybersecurity professionals’ recommendations include adhering to established security standards, including encryption and access permissions (Stewart, 2022). In accordance to these protocols, EUMC can retain the feasibility of patient specific information protection, therefore minimizing the possibility of violations and breaches.
Continuous monitoring and the measures contained in an incident response plan guarantee early detection of the security incidents. This proactive approach, allows EUMC to prevent the consequences of breaches from being felt on the side of the patient’s privacy or the organization’s functioning while ensuring that the organization upholds the aspects of integrity and trust (Koopmans & Mouter, 2020).
Continuing to abide by everyday regulatory standards such as HIPAA or GDPR is crucial to prevent fines and patients’ information leakage. Therefore, through following the above stipulated standards and undertaking assessments as and when necessary, EUMC upholds legal and ethical practices, which enhances patients and stakeholders’ confidence.
Encryption of patient information and measures to limit the access, as pointed out by Alkinoon et al. (2021), enhance EUMC security measures against unlawful access to patients’ records. These measures also incorporate compliance with the norms set within the medical industry as well as protect patient’s rights, and guarantee the organization’s ethical standards. mandatory cybersecurity training educates the employees of EUMC decreasing the possibility for human factor to be the reason for a breach.
This way, EUMC develops among its staff the readiness to safeguard patient information thus boosting the patients’ confidence in the healthcare services provided by EUMC (Shukla et al. , 2022). In general, incorporating such evidence-based recommendations enhances EUMC’s data security measures and reduces potentials vulnerabilities and threats of a breach as well as protect patient’s confidentiality and ensure patients trust in the organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the research study on the policies, procedures, and experience of data collection and analysis concerning data breaches at Emory University Medical Center has offered insights and suggestions on the enhancement of data protection.
This assessment will thus help EUMC improve on the identified aspects to gain better control and intolerate breach risks as recommended by available evidence. Therefore, for the future work, it will be necessary to continue the implementation of the provided recommendations that include the deepening of cybersecurity awareness for workers and the development of data encryption and incident response policies to protect patients’ data and trust in EUMC healthcare services from further cyber threats.
If you need complete information about class 4020, click below to view a related sample:
BHA FPX 4020 Assessment 2 Health Care Professional Feedback
References
Ahmad, A., Desouza, K. C., Maynard, S. B., Naseer, H., & Baskerville, R. L. (2019). How integration of cyber security management and incident response enables organizational learning. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 71(8), 939–953.
https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.24311
Algarni, A. M., Thayananthan, V., & Malaiya, Y. K. (2021). Quantitative assessment of cybersecurity risks for mitigating data breaches in business systems. Applied Sciences, 11(8), 3678.
https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083678
Alkinoon, M., Choi, S. J., & Mohaisen, D. (2021). Measuring healthcare data breaches. Information Security Applications, 265–277.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89432-0_22
Bandari, V. (2023). Enterprise data security measures: A comparative review of effectiveness and risks across different industries and organization types. International Journal of Business Intelligence and Big Data Analytics, 6(1), 1–11.
https://research.tensorgate.org/index.php/IJBIBDA/article/view/3
Biancardo, S. A., Gesualdi, M., Savastano, D., Intignano, M., Henke, I., & Pagliara, F. (2022). An innovative framework for integrating Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) within Building Information Modeling (BIM). Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 101495.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2022.101495
Campbell, K., Gordon, L. A., Loeb, M. P., & Zhou, L. (2023). The economic cost of publicly announced information security breaches: empirical evidence from the stock market. Journal of Computer Security, 11(3), 431–448.
https://doi.org/10.3233/jcs-2003-11308
D’Arcy, J., Adjerid, I., Angst, C. M., & Glavas, A. (2020). Too good to be true: Firm social performance and the risk of data breach. Information Systems Research, 31(4), 1200–1223.
https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.2020.0939
Dagher, G. G., Mohler, J., Milojkovic, M., & Marella, P. B. (2019). Ancile: Privacy-preserving framework for access control and interoperability of electronic health records using blockchain technology. Sustainable Cities and Society, 39, 283–297.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2018.02.014
Kampová, K., Mäkká, K., & Zvaríková, K. (2020). Cost-benefit analysis within organization security management. School of Health Sciences Web of Conferences, 74, 01010.
https://doi.org/10.1051/shsconf/20207401010
Koopmans, C., & Mouter, N. (2020, January 1). Chapter One – Cost-benefit analysis (N. Mouter, Ed.). ScienceDirect; Academic Press.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2543000920300184
Kush, R. D., Warzel, D., Kush, M. A., Sherman, A., Navarro, E. A., Fitzmartin, R., Pétavy, F., Galvez, J., Becnel, L. B., Zhou, F. L., Harmon, N., Jauregui, B., Jackson, T., & Hudson, L. (2020). FAIR data sharing: The roles of common data elements and harmonization. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 107, 103421.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2020.103421
Mouter, N., Dean, M., Koopmans, C., & Vassallo, J. M. (2020, January 1). Chapter Seven – Comparing cost-benefit analysis and multi-criteria analysis (N. Mouter, Ed.). ScienceDirect; Academic Press.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2543000920300226
Nield, J., Scanlan, J., & Roehrer, E. (2020). Exploring consumer information-security awareness and preparedness of data-breach events. Library Trends, 68(4), 611–635.
