NURS 6501 Week 8 Assignment FREE DOWNLOAD
NURS 6501 Week 8 Assignment
Case Study Analysis
Student Name
Walden University
NURS 6501: Advanced Pathophysiology
Professor Name
Date
Week 8: Case Study Analysis
Key Symptoms Presented
A 44-year-old male patient is unable to stand on his afflicted leg and has severe pain, edema, and redness in his left knee. He says he has toe discomfort as well. While denying symptoms like fever and rash or any severe injury, he had symptoms that began in his knee throughout the course of the four drinks he had consumed. Since the patient exhibits acute monoarticular joint inflammation that primarily affects his knee joint and may also spread to his first metatarsophalangeal joint, gout becomes the most likely diagnosis (Cha et al., 2024). The diagnostic evidence includes high inflammatory markers, such as uric acid levels of 8 mg/dL, CRP of 10.5 mg/dL, and ESR of 65 mm/hr., as well as synovial fluid tests for monosodium urate crystals. Acute gout flare is the primary reason, not any other arthritis or joint infection, as determined by the combination of lab and medical data, which rules out any other possibilities.
Musculoskeletal Pathophysiologic Processes
Elevated blood uric acid causes MSU crystals to accumulate in joints, leading to the development of gout. Purine metabolism produces uric acid, which then surpasses the solubility threshold to crystallize and settle inside synovial joints, affecting colder peripheral joints like the knees and toes. When crystals trigger the immune system, neutrophils and macrophages respond, releasing the inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β (Oliviero et al., 2020). This inflammatory reaction results in joint swelling, redness, and warmth in addition to excruciating pain. When synovial fluid accumulates in the joints, it becomes difficult to move and stand on the afflicted foot. The pathophysiological features of acute gouty arthritis are matched by the inflammatory symptoms present in both joint tissues in this instance.
Role of Obesity in Progression
An increased risk of developing osteoarthritis and gout is associated with obesity. By increasing purine metabolism and decreasing kidney function for uric acid clearance, primarily due to insulin resistance, physical obesity with a BMI of 32 causes hyperuricemia (Gong et al., 2020). Gout is made worse by the inflammatory mediators that adipose tissue produces. Obesity causes excess weight, which increases stress on weight-bearing knees and accelerates the deterioration of cartilage, leading to osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis-related joint deterioration may make the environment more prone to urate crystal deposition, which would raise the risk of knee gout (Motta et al., 2022). Therefore, obesity contributes to joint illness both mechanically and metabolically.
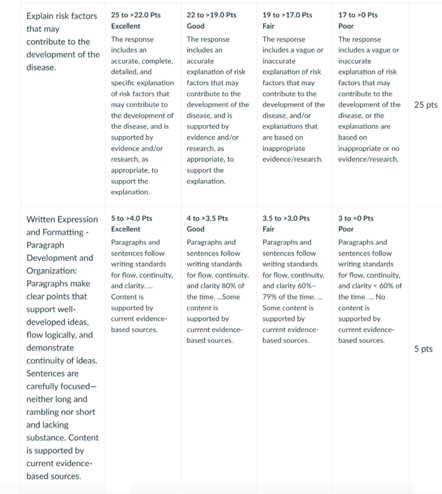
Risk Factors for Development of Disease
Gout develops as a result of several risk factors, many of which this patient possesses. Drinking alcohol, especially beer, is a common cause of gout because it raises the formation of uric acid and lowers renal excretion. This flare was probably caused by the recent drinking of four beers. Another important consideration is the use of hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension; thiazide diuretics reduce renal uric acid excretion, which leads to hyperuricemia (Sanchez-Lozada et al., 2020). As was previously mentioned, obesity increases systemic inflammation and uric acid levels. The patient may experience small trauma and repetitive joint stress as a result of occupational strain from their profession as a floor installer, which might exacerbate joint inflammation and injury. Other non-modifiable risk variables include male sex and genetic susceptibility; however, they were not mentioned in the instance.
Struggling with your NURS 6501 Week 4 Assignment Case Study Analysis? Get expert help now!
Instructions To Write NURS 6501 Week 8 Assignment
Need instructions for this assessment? Contact us now and get expert guidance right away!
Instructions File For 6501 Week 8 Assignment
CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
An understanding of the musculoskeletal systems is a critically important component of disease and disorder diagnosis and treatment. This importance is magnified by the impact that that this system may have on another. A variety of factors and circumstances affecting the emergence and severity of issues in one system can also have a role in the performance of the other.
Effective analysis often requires an understanding that goes beyond these systems and their mutual impact. For example, patient characteristics such as, racial and ethnic variables can play a role.
An understanding of the symptoms of alterations in musculoskeletal systems is a critical step in diagnosis and treatment. For APRNs this understanding can also help educate patients and guide them through their treatment plans.
In this Assignment, you examine a case study and analyze the symptoms presented. You identify the elements that may be factors in the diagnosis, and you explain the implications to patient health.
RESOURCES
Be sure to review the Learning Resources before completing this activity.
Click the weekly resources link to access the resources.
WEEKLY RESOURCES
To prepare:
By Day 1 of this week, you will be assigned to a specific case study scenario for this Case Study Assignment. Please see the “Announcements” section of the classroom for your assignment from your instructor.
The Assignment (1- to 2-page case study analysis)
Develop a 1- to 2-page case study analysis by answering the questions provided following the case scenario.
BY DAY 7 OF WEEK 8
Submit your Case Study Analysis Assignment by Day 7 of Week 8.
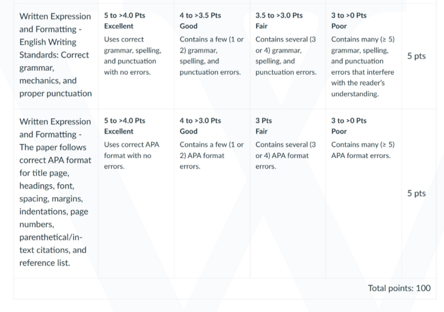
Reminder: The College of Nursing requires that all papers submitted include a title page, introduction, summary, and references. The sample paper provided at the Walden Writing Center provides an example of those required elements (available at
https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/templates). All papers submitted must use this formatting.
SUBMISSION INFORMATION
Before submitting your final assignment, you can check your draft for authenticity. To check your draft, access the Turnitin Drafts from the Start Here area.
To submit your completed assignment, save your Assignment as
WK8Assgn2_LastName_FirstInitialThen, click on Start Assignment near the top of the page.
Next, click on Upload File and select Submit Assignment for review.
NURS 6501 Week 8 Assignment Rubrics

References For NURS 6501 Week 8 Assignment
Cha, Y., Lee, J., Choy, W., Jae Sun Lee, Hyun Hee Lee, & Chae, D.-S. (2024). Pathophysiology and treatment of gout arthritis; including gout arthritis of hip joint: A literature review. Hip and Pelvis, 36(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2024.36.1.1
Gong, M., Wen, S., Nguyen, T., Wang, C., Jin, J., & Zhou, L. (2020). Converging relationships of obesity and hyperuricemia with special reference to metabolic disorders and plausible therapeutic implications. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy, Volume 13, 943–962. https://doi.org/10.2147/dmso.s232377
Motta, F., Barone, E., Sica, A., & Selmi, C. (2022). Inflammaging and osteoarthritis. Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology, 64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-022-08941-1
Oliviero, F., Bindoli, S., Scanu, A., Feist, E., Doria, A., Galozzi, P., & Sfriso, P. (2020). Autoinflammatory mechanisms in crystal-induced arthritis. Frontiers in Medicine, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.00166
Sanchez-Lozada, L. G., Rodriguez-Iturbe, B., Kelley, E. E., Nakagawa, T., Madero, M., Feig, D. I., Borghi, C., Piani, F., Cara-Fuentes, G., Bjornstad, P., Lanaspa, M. A., & Johnson, R. J. (2020). Uric Acid and hypertension: An update with recommendations. American Journal of Hypertension, 33(7), 583–594. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpaa044
Best Professors To Choose From For NURS 6501 Class
- Dr. Mary Smith
- Dr. Tara Harris
- Dr. Mahaman Moussa
- Dr. Annaliza (Anna Liza) Villena
- Dr. Morgan Skinner
(FAQs) related to NURS 6501 Week 8 Assignment
Question 1: Where can I download a free sample for NURS 6501 Week 8 Assignment?
Answer 1: Download a free sample from Tutors Academy.
Question 2: Where can I find the rubrics and instruction file for NURS 6501 Week 8 Assignment?
Answer 2: Get the rubric and instruction file from the Tutors Academy website.
Do you need a tutor to help with this paper for you with in 24 hours.
- 0% Plagiarised
- 0% AI
- Distinguish grades guarantee
- 24 hour delivery

