
- RSCH FPX 7864 Assessment 4 Data Analysis Plan.
Data Analysis Plan
The ANOVA for a single factor, a significant tool in data analysis, can be performed using the grades.asp file from the database. It is a method of splitting diversity within the data into units that can be tested further (Kenton, 2021). This method is particularly useful when comparing two or more unrelated groups. The groups in question can be distinguished by certain characteristics, and the ANOVA test helps to identify any significant differences. The variables used in this context are Quiz 3 and Sections, which represent classified and unclassified variables. Quiz 3, however, is performance-based and continuous.
The study question is: What is the difference between the mean scores of students in different groups on Quiz 3?
The null hypothesis, a crucial component of the ANOVA test, states that differences between the mean scores of students in various groups on Quiz 3 are insignificant. This hypothesis forms the basis of our analysis and guides our interpretation of the results.
Conversely, the alternative hypothesis suggests that the mean scores of students in different groups on Quiz 3 are significantly different, indicating a high level of variance.
Testing Assumptions
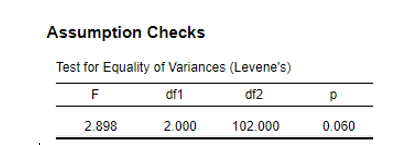
Levene’s test determines if the means of two or more groups are equal (SPSS Tutorials, 2019). It is applied in inferential statistics. The test results will demonstrate that the null hypothesis is false and the variance among groups is equal. This means that there is a significant difference between the mean scores of students in various groups on Quiz 3, and this difference is not due to random chance. The p number of the test is 0.6, which is not 0.5 but more than it, so p > .05. Thus, the null theories can never be eliminated, and uniformity is achieved.
Results & Interpretation
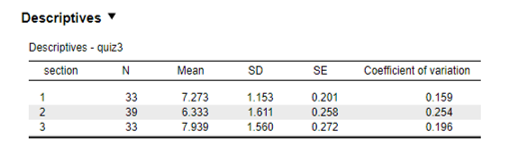
All three students got the same score on Quiz 3. The table below shows what we can say.
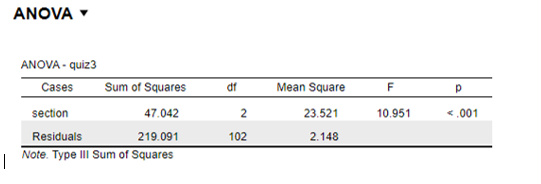
This was achieved using the one-way ANOVA. Quiz 3 was grouped into three sets of scores. As can be seen from the table below, F (2, 102) =10.95, p <.001, which indicates that the null hypothesis, which states that there is no difference between the mean scores of three groups of students on Quiz 3, is rejected.
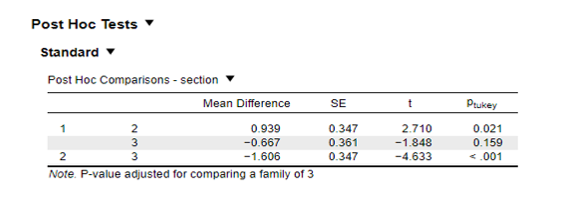
The HSD for Turkey (Frost, 2019) was used for the post hoc analysis. The difference between section 1 and section 2 is significant (p <.05) has been found. This is the reason the null theory fails. As no significant data were found between parts 3 and 1, null hypothesis could not be rejected (p >.05.). In parts 2 and 3, the null hypothesis is rejected as p is less than .05.
Statistical Conclusions
Using ANOVA and Omnibus Test for Analyzing Quantitative Data
When one variable is qualitative and independent, and the other is quantitative and dependent, the ANOVA test is used—the levels or groups of the independent variable. Two groups can be compared using one test. When many pairwise tests are conducted on the data, ANOVA sometimes wrongly rejects a true null hypothesis.
The omnibus test helps to avoid the error of rejecting a theory that is true (Ceri & Cicek, 2020). The omnibus test only has one flaw: it notes an issue but does not qualify it. The third and second quizzes were compared using the one-way ANOVA, which revealed they were significantly different.
Interpreting p-Values and F-Statistics in ANOVA Analysis
Some things are impossible when using ANOVA to compare data from two or more groups. The p-value informs us of the dissimilarity of the two data sets. It demonstrates the student’s performance on the post-hoc test for Quiz 3. From the given data, a p-value less than 0.5 suggests that the null hypothesis can be rejected. Hence, F is significant, and the mean of Quiz 3 is at least one pair homogeneous to the other two. Given p > .05, the null hypotheses in sections 1 and 3 should not be rejected.
Application
Understanding the Role and Applications of ANOVA in Research
The ANOVA test concerns the influence of the means of two or more groups on one or more factors. It also helps determine the similarity of the groups and keeps the type 1 error rate under control (if we have a false positive) in psychology (Ceri & Cicek, 2020). The comparison of the two groups is done using the ANOVA test.
For instance, it is used to know how mood, diet, and hormones impact mouse models of Alzheimer’s. The two-way ANOVA enables one to determine if medicine and age are related. It helps identify which differences between the means are essential. ANOVA can be used to see if the treatment makes mental suffering even worse (Pok-Ja Cho & Ran, 2020). Explore our blog RSCH FPX 7864 Assessment 1 Descriptive Statistics for complete information about this class.
References
Ceri, V., & Cicek, I. (2020). Psychological well-being, depression and stress during COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey: A comparative study of healthcare professionals and non-healthcare professionals. Psychology, Health & Medicine, 26(1), 1–13.
https://doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2020.1859566
Frost, J. (2019, January 14). Using Post Hoc Tests with ANOVA. Statistics by Jim.
https://statisticsbyjim.com/anova/post-hoc-tests-anova/
Kenton, W. (2021, October 6). Analysis of Variance – ANOVA. Investopedia.
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/a/anova.asp
Pok-Ja Cho, Oh., & Ran, J. (2020). Changes in Fatigue, Psychological Distress, and Quality of Life After Chemotherapy in Women with Breast Cancer: A Prospective Study. Journals.lww.com.
https://doi.org/10.1097/NCC.0000000000000689
SPSS Tutorials. (2019). Levene’s Test – Quick Introduction. Spss-Tutorials.com.
