NURS 6521 Week 4 Assignment FREE DOWNLOAD
NURS 6521 Week 4
Case Studies
Student Name
Walden University
NURS 6521
Professor Name
Date
Case Studies
In clinical practice, proper prescription writing, good planning of treatment and decision making based on guidelines are crucial to optimum patient outcomes. The given paper will examine four different clinical cases related to medication errors, the management of asthma in an adolescent, hypertension in an African American adult, and diabetes in a patient with renal impairment. The evidence-based guidelines used to review each case include JNC 8, ACC/AHA, ADA, and GINA, and therefore, the recommendations are up to date. By addressing the error of prescription, changing therapeutic regimes, and offering a lot of patient education, the following answers are supposed to facilitate the enhancement of safety, adherence, and the long-term health outcomes.
Prescription Corrections
In the first case, there are five prescriptions that need to be corrected and clarified. The first one is 5 mg of linagliptin, which is not accompanied by standardised instruction. The order corrected is: linagliptin 5 mg tablet, 1 tab by mouth q day, dispense #30, refill 5. Linagliptin is a DPP-4 inhibitor that raises the level of incretin hormones to raise insulin secretion and lower glucagon and controls blood sugar in type 2 diabetes. The second medicine, Tresiba (insulin degludec) is prescribed wrongly as 10 units SC TID with meals. Tresiba is a long-acting basal insulin which is not to be used with meals (Mehta et al., 2021). The correct regimen must be: Insulin degludec 10 units SC qd at same time each day, dispone one box (five pens), one refill. This insulin is bound to albumin and is released gradually within 24 hours or more giving constant glucose control.
Tiotropium (Spiriva) was erroneously labeled to be taken orally 2.5 mcg PO BID. Since it is a bronchodilator which is taken by inhaling it, the corrected prescription will read: Tiotropium 2.5 mcg/actuation, two puffs once daily using Respimat inhaler, dispense one inhaler, one refill. Tiotropium is a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) that acts by blocking cholinergic receptors and, as a result, causing airways relaxation (Cazzola et al., 2021). Qulipta (atogepant) was wrongly classified as 60 mg PRN migraine, but is instead used as a daily prevention medication, rather than a treatment medication. The rewritten notation is: Atogepant 60 mg tablet, 1 tab by mouth once-a-day, dispense 30, one refill. This drug antagonizes CGRP receptors that are important in the pathophysiology of migraine.
The last prescription, levothyroxine 88 mcg, ought to be based on the time of administration. It should be arranged as follows: Levothyroxine 88 mcg tablet, one tablet orally, without food, 30 to 60 minutes before breakfast, disp #30, five refills. Levothyroxine supplements the internal thyroid hormone and maintains metabolism and energy.
Asthma Management in Adolescents
In the second scenario, PK is a 16-year-old female with mild persistent asthma, whereby frequent night symptoms and overuse of her albuterol inhaler were noted. Her symptoms are not controlled well despite the fluticasone MDI. The guidelines of the 2022 Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) recommend a more effective regimen to include an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) combined with formoterol, a long-acting beta agonist and an agent that can be used both as maintenance therapy and as needed (Levy et al., 2023).
The suitable plan of treatment would involve switching her to formoterol-budesonide: Symbicort 160/4.5 mcg per puff, inhale two puffs twice daily and one to two puffs as needed, dispense two inhalers of 120 puffs each, two refills. The method enables both anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator properties and makes the regime easier to follow. Albuterol should not be overused because it can aggravate the inflammation and lead to an increase in risks of exacerbation.
Sedating antihistamine like diphenhydramine is not supposed to be used because it is dangerous in adolescents (Clark et al., 2025). An allergic symptom may be continued with a non-sedating antihistamine like fexofenadine. Monitoring is to be performed through an asthma control test (ACT) and instruction on good inhaler techniques. The patient is advised to come back after four to six weeks and get his symptom control reassessed and possibly change his dose. Moreover, PK needs to be taught about triggers avoidance, the usage of inhalers, and the necessity of therapy compliance.
Hypertension in African American Male
The third case is about ES, a 45-year-old African American male, whose blood pressure is elevated (142/89 mmHg), and the heart rate is 60 bpm. He irregularly receives bisoprolol with side effects as the excuse. JNC 8 and ACC/AHA support the use of thiazide-type diuretics or calcium channel blockers as first-line agents in African American adults since they are more effective and show better cardiovascular outcomes in this group of patients (Ogunniyi et al., 2021).
Bisoprolol should be withdrawn since the patient has no strong indication of the beta-blocker treatment (e.g. heart failure or post-MI). An alternative remedy is a calcium channel blocker such as amlodipine. The updated prescription is as follows: Amlodipine 5 mg tablet, one tablet orally q day, disp #30, two refills. Amlodipine is an agent that facilitates vasodilation through the blockage of calcium entry into the vascular smooth muscle (Cole et al., 2022).
The goal blood pressure of ES is less than 130/80 mm Hg. Education of the patients is necessary and they should be advised about lifestyle changes such as the DASH diet, sodium restriction, exercise, and weight loss. The patient must be informed about the necessity of taking medication every day despite the absence of the symptoms. The next visit should be within two to four weeks to evaluate the efficiency and the tolerability of the new drug.
Diabetes and Renal Impairment
TF is a 60-year-old male who has diabetes type 2 and moderate-severe chronic kidney disease (eGFR 28 mL/min/1.73 m 2). His A1C is high at 8.5%, which means that he should have a stronger glycemic control. He is taking donepezil and atorvastatin medications, and it is not evident that he is getting good diabetic treatment. A number of agents are inadvisable or contraindicated because of his renal status.
Sulfonylureas, glyburide and glimepiride, are not advised as these drugs pose an enhanced risk of hypoglycemia to patients with impaired kidneys (Tomlinson et al., 2021). Sitagliptin and metformin have to be dosed and used cautiously. Nevertheless metformin can be continued at low dosage in case it is tolerated and risk of lactic acidosis is low. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist like semaglutide is suitable because of the renal and cardiovascular advantage. It must be prescribed as follows: Semaglutide 0.25 mg subcutaneously once a week, dispense one pen, two refills. Increase to 0.5 mg at four weeks provided tolerated.” The mechanism of the semaglutide action is the stimulated glucose-dependent secretion of insulin and the decreased gastric emptying, which results in the drop in postprandial glucose and weight reduction (Alorfi & Algarni, 2022).
Although canagliflozin can also be renal protective, it is less effective in patients with eGFR less than 30. Thus, it must not be used or used under expert advice. The ideal A1C target of the patient should be less than 7.0 percent, though <8.0 percent might be acceptable according to overall health conditions. It is suggested to follow up after every three months and monitor BMP as well as counsel a patient about possible side effects in the gastrointestinal tract.
Conclusion
In conclusion, clinical decision-making entails accurate prescription writing, case-by-case patient evaluation, and compliance with evidence-based treatment protocols. In the initial case, medication errors were corrected, and this enhanced clarity and safety. In the second, management of adolescent asthma was updated to match with the GINA guidelines with the ICS formoterol dual therapy. The third case indicated the necessity of considering the antihypertensive agents according to racial and individual characteristics of patients and making a change to amlodipine to manage it better than a beta-blocker. Lastly, the fourth case scenario covered the complicated nature of treating diabetes in a patient with renal impairment with semifluid as a good choice of agent and the avoidance of sulfonylureas. By performing such analyses, patient safety, curative performance, and compliance with the existing standards of clinical practice were put on priority so that the best results are achieved.
Instructions To Write NURS 6521 Week 4 Assignment
Need instructions for this assessment? Contact us now and get expert guidance right away!
Instructions File For 6521 Week 4 Assignment
ASSIGNMENT: CASE STUDIES
Case studies are a useful way for you to apply your knowledge of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic aspects of pharmacology to specific patient cases and health histories.
For this Assignment, you evaluate drug treatment plans for patients with various disorders and justify drug therapy plans based on patient history and diagnosis.
RESOURCES
Be sure to review the Learning Resources before completing this activity.
Click the weekly resources link to access the resources.
WEEKLY RESOURCES
To Prepare:
Review the case study posted in “Announcements” by your Instructor for this Assignment
Review the information provided and answer questions posed in the case study
When recommending a medication, write out a complete prescription for the medication
Whenever possible, use clinical practice guidelines in developing your answers when possible
Include at least three references to support your answer and cite them in APA format
BY DAY 7 OF WEEK 4
Submit the Assignment.
SUBMISSION INFORMATION
Before submitting your final assignment, you can check your draft for authenticity. To check your draft, access the Turnitin Drafts from the Start Here area.
To submit your completed assignment, save your Assignment as WK4Assgn_LastName_Firstinitial
Then, click on Start Assignment near the top of the page.
Next, click on Upload File and select Submit Assignment for review.
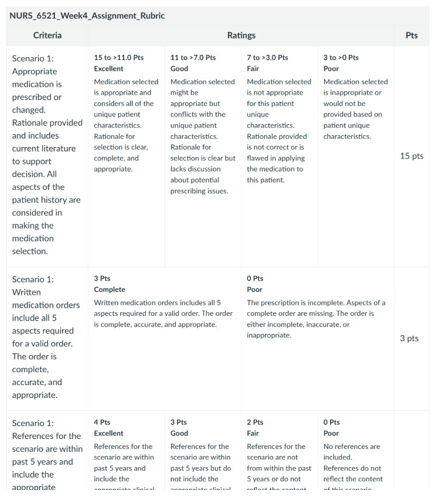
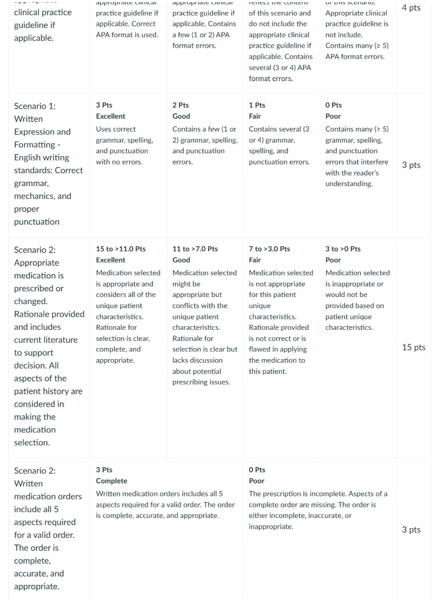
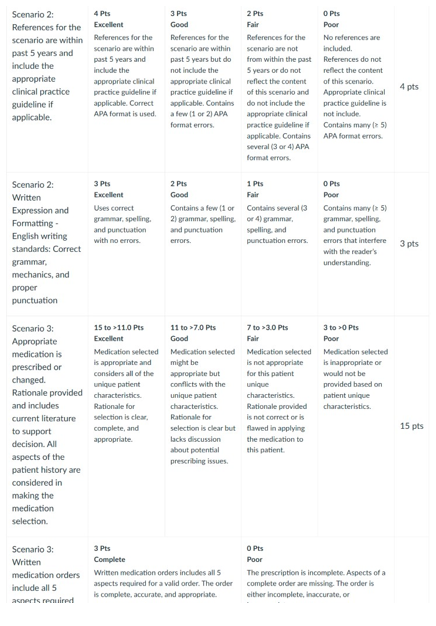
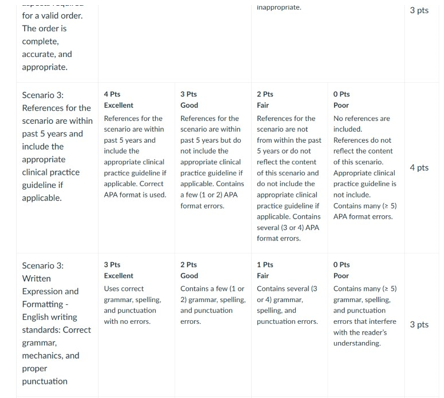
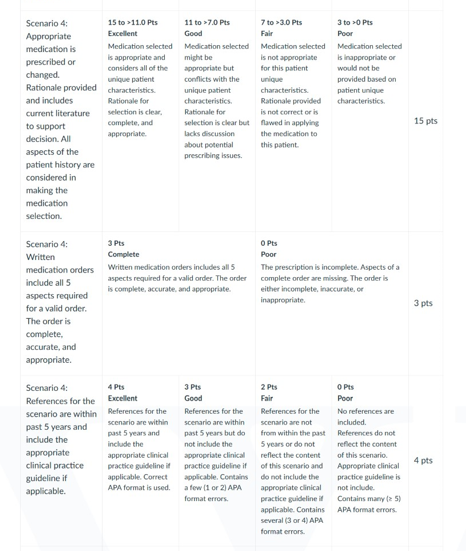
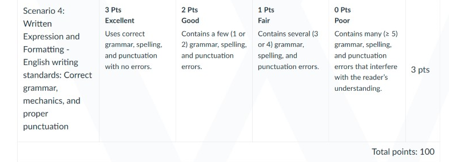
NURS 6521 Week 4 Assignment Rubrics
References For NURS 6521 Week 4 Assignment
Alorfi, N. M., & Algarni, A. S. (2022). Clinical impact of semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, on obesity management: A review. Clinical Pharmacology: Advances and Applications, Volume 14, 61–67. https://doi.org/10.2147/cpaa.s374741
Cazzola, M., Calzetta, L., & Matera, M. G. (2021). Long‐acting muscarinic antagonists and small airways in asthma: Which link? Allergy. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.14766
Clark, J. H., Meltzer, E. O., & Naclerio, R. M. (2025). Diphenhydramine: It is time to say a final goodbye. World Allergy Organization Journal, 18(2), 101027–101027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.waojou.2025.101027
Cole, J. C., Lee, S. C., Prekker, M. E., Kunzler, N. M., Considine, K. A., Driver, B. E., Puskarich, M. A., & Olives, T. D. (2022). Vasodilation in patients with calcium channel blocker poisoning treated with high-dose insulin: A comparison of amlodipine versus non-dihydropyridines. Clinical Toxicology, 60(11), 1205–1213. https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2022.2131565
Levy, M. L., Bacharier, L. B., Bateman, E., Boulet, L.-P., Brightling, C., Buhl, R., Brusselle, G., Cruz, A. A., Drazen, J. M., Duijts, L., Fleming, L., Inoue, H., Ko, F. W. S., Krishnan, J. A., Mortimer, K., Pitrez, P. M., Sheikh, A., Yorgancıoğlu, A., & Reddel, H. K. (2023). Key recommendations for primary care from the 2022 global initiative for Asthma (GINA) update. NPJ Primary Care Respiratory Medicine, 33(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41533-023-00330-1
Mehta, R., Goldenberg, R., Katselnik, D., & Kuritzky, L. (2021). Practical guidance on the initiation, titration, and switching of basal insulins: A narrative review for primary care. Annals of Medicine, 53(1), 999–1010. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2021.1925148
Ogunniyi, M. O., Commodore-Mensah, Y., & Ferdinand, K. C. (2021). Race, ethnicity, hypertension, and heart disease: JACC Focus Seminar 1/9. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 78(24), 2460–2470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2021.06.017
Tomlinson, B., Patil, N. G., Fok, M., Chan, P., & Lam, C. W. K. (2021). The role of sulfonylureas in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy, 23(3), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/14656566.2021.1999413
Best Professors To Choose From For NURS 6521 Class
- Aaron Weiner
- Stephanie Stanton
- Claudia Robin
- Katherine Gryzenia
- Christopher Bradley
(FAQs) related to NURS 6521 Week 4 Assignment
Question 1: Where can I download a free sample for NURS 6521 Week 4 Assignment?
Answer 1: Download a free sample from Tutors Academy.
Question 2: Where can I find the rubrics and instruction file for NURS 6521 Week 4 Assignment?
Answer 2: Get the rubric and instruction file from the Tutors Academy website.
Do you need a tutor to help with this paper for you with in 24 hours.
- 0% Plagiarised
- 0% AI
- Distinguish grades guarantee
- 24 hour delivery

