NURS 6501 Week 7 Assignment FREE DOWNLOAD
NURS 6501 Week 7 Assignment
Neurological Disorders
Student Name
Walden University
NURS 6501: Advanced Pathophysiology
Professor Name
Date
Concept Map Template
Primary Diagnosis: Parkinson’s Disease
Describe the pathophysiology of the primary diagnosis in your own words. What are the patient’s risk factors for this diagnosis?
Pathophysiology of Primary Diagnosis | |
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological condition that deteriorates the body’s movement system over time. Dopamine is necessary for regulating smooth muscle activity, and a significant breakdown or death of nerve cells across the substantia nigra results in a dopamine deficiency (Salvatore, 2024). Classic diagnostic symptoms include stiff, trembling motions, slowed movement, and balance problems are caused by low dopamine levels between brain regions and muscular control. Although a number of risk factors increase the possibility that Parkinson’s disease may manifest, scientists have not yet determined the exact cause of neuron degeneration in this condition. People over the age of 60, as well as males, are more likely to get Parkinson’s disease, as are those who have been exposed to pesticides or heavy metals, and those who have a family history of the condition (Chambers-Richards et al., 2023). | |
Causes | Risk Factors (genetic/ethnic/physical) |
· Loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra (part of the brain that controls movement). · Presence of Lewy bodies (abnormal protein clumps, primarily alpha-synuclein) (Mukherjee et al., 2022). · Dopamine and acetylcholine neurotransmitters are imbalanced in the brain. · Researchers have not found particular causes for this illness, which medical science refers to as ‘idiopathic.’ · Parkinson’s disease can occasionally be caused by genetic abnormalities affecting LRRK2, PARK7, and PINK1. | Genetic · Family history of Parkinson’s disease · Certain genes such as LRRK2 along with SNCA contain inherited mutations which cause this condition (Jia et al., 2022). Ethnic · Research shows Caucasian people experience a greater risk compared to African and Asian communities although specific results differ Physical / Environmental · Degeneration of dopaminergic cells becomes more likely starting at age 60 forward. · More common in men than women · Long-term exposure to pesticides, herbicides, and heavy metals · People residing in rural places are at higher risk due to environmental exposures. · History of head trauma · Chronic stress or inflammation (possible contributing factor) |
What are the patient’s signs and symptoms for this diagnosis? How does the diagnosis impact other body systems and what are the possible complications?
Signs and Symptoms – Common presentation | How does the diagnosis impact each body system? Complications? |
Motor Symptoms (hallmark features) · A resting tremor (which begins in one hand) represents one feature of motor symptoms. · Bradykinesia (slowness of movement) · Muscle rigidity (stiffness, resistance to movement) · Postural instability (balance problems, frequent falls) Non-Motor Symptoms · Depression, anxiety, mood changes · Sleep disturbances (insomnia, REM sleep behavior disorder) · Cognitive changes (memory issues, confusion, eventually dementia) · Loss of sense of smell (anosmia) · Constipation, urinary urgency or incontinence · Fatigue and low energy | · The steady loss of dopamine in the nerve system causes brain processes to decline, resulting in movement disorders, mood changes, and cognitive problems (Duan et al., 2024). · Muscular stiffness combined with tremors reduces an individual’s freedom of movement and has a detrimental impact on coordination and muscular strength. · The GI tract slows its motions, resulting in constipation and bloating. · Patients with bladder dysfunction suffer both an acute need to pee and the inability to control their bladder functions. · The cardiovascular system may suffer from dysfunctions in the autonomic nervous system, resulting in low blood pressure and dizziness. · Respiratory System abnormalities can emerge in the late stages when muscular control of breathing deteriorates, increasing the risk of both aspiration and pneumonia. Complications · Patients face an elevated danger of losing their balance along with breaking bones. · Dementia and severe cognitive decline in later stages · The impairment of daily life becomes worse because of depression and anxiety. · The condition of dysphagia makes it difficult for patients to swallow which results in both malnutrition along with aspiration pneumonia. · Patients experience involuntary movements (dyskinesia) along with hallucinations as side effects from their medications (Simonet et al., 2019). |
What are other potential diagnoses that present in a similar way to this diagnosis (differentials)?
· Essential tremor presents with shaking during movement rather than at rest and does not involve muscle stiffness or slowed movement. · Drug-induced parkinsonism is caused by medications such as antipsychotics and often improves after stopping the drug. · Multiple system atrophy resembles Parkinson’s but includes more severe problems with blood pressure control and bladder function. · Progressive supranuclear palsy can cause early balance issues and difficulty with eye movements, especially looking up or down (Kassavetis et al., 2022). · Corticobasal degeneration often shows stiffness and poor coordination on one side of the body along with involuntary movements. · Lewy body dementia includes Parkinson-like symptoms but with early-onset memory loss, confusion, and visual hallucinations. · Normal pressure hydrocephalus presents with walking difficulty, memory problems, and urinary incontinence, which can mimic Parkinson’s disease. |
What diagnostic tests or labs would you order to rule out the differentials for this patient or confirm the primary diagnosis?
|
What treatment options would you consider? Include possible referrals and medications.
· The most effective medicine to alleviate motor symptoms is levodopa/carbidopa, which replaces dopamine in the brain (Armstrong & Okun, 2020). · Dopamine agonists, such as pramipexole or ropinirole, can be taken alone or in combination with Levodopa to activate dopamine receptors. · MAO-B inhibitors, such as selegiline or rasagiline, assist prevent dopamine breakdown and can improve the efficacy of other drugs (Armstrong & Okun, 2020). · Entacapone, a COMT inhibitor, is occasionally given to Levodopa to extend its efficacy. · Anticholinergic drugs can be used in younger individuals to assist reduce tremors, although they are less typically utilized owing to cognitive adverse effects. · Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure for individuals with severe motor symptoms that are not effectively managed by medicines. · Physical therapy referrals can assist improve mobility, strength, and balance, lowering the risk of falling. |
Unlock expert help for your NURS 6501 Week 4 Assignment Case Study Analysis. Get started now!
Instructions To Write NURS 6501 Week 7 Assignment
Need instructions for this assessment? Contact us now and get expert guidance right away!
Instructions File For 6501 Week 7 Assignment
NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
In this exercise, you will complete a MindMap to gauge your understanding of this week’s content. Select one of the possible topics provided to complete your MindMap assignment:
Stroke
Multiple sclerosis
Transient ischemic Attack
Myasthenia gravis
Headache: May choose – migraine, cluster, tension
Seizure disorders: Adults or Children
Brain injury
Alzheimer Disease
Neuroblastoma
Parkinson’s Disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Degenerative Disorders of the Spine: May choose – Low back pain, Degenerative Disc Disease
RESOURCES
Be sure to review the Learning Resources before completing this activity. Click the weekly resources link to access the resources.
WEEKLY RESOURCES
BY DAY 7 OF WEEK 7
Submit your MindMap by Day 7 of Week 7.
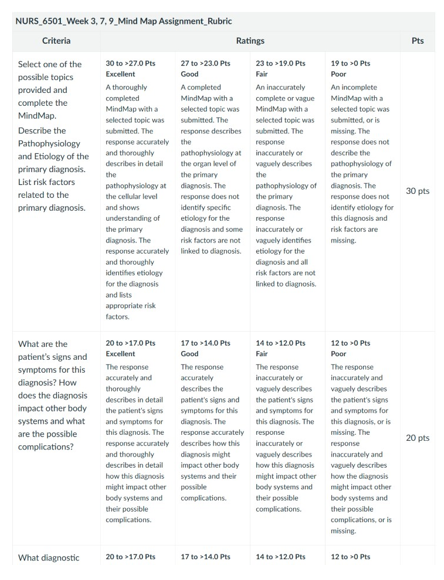
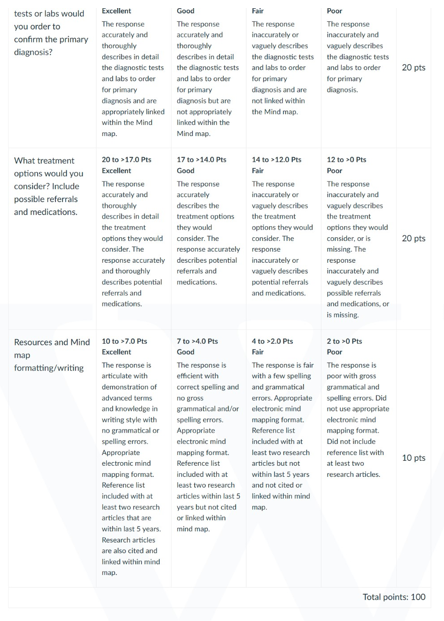
NURS 6501 Week 7 Assignment Rubrics
References For NURS 6501 Week 7 Assignment
Armstrong, M. J., & Okun, M. S. (2020). Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease. JAMA, 323(6), 548–560. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.22360
Chambers-Richards, T., Su, Y., Chireh, B., & D’Arcy, C. (2023). Exposure to toxic occupations and their association with Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Reviews on Environmental Health, 38(1), 65–83. https://doi.org/10.1515/reveh-2021-0111
Duan, X., Liu, H., Hu, X., Yu, Q., Kuang, G., Liu, L., Zhang, S., Wang, X., Li, J., Yu, D., Huang, J., Wang, T., Lin, Z., & Xiong, N. (2024). Insomnia in Parkinson’s disease: Causes, consequences, and therapeutic approaches. Molecular Neurobiology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-024-04400-4
Jia, F., Fellner, A., & Kumar, K. R. (2022). Monogenic Parkinson’s disease: Genotype, phenotype, pathophysiology, and genetic testing. Genes, 13(3), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13030471
Kassavetis, P., Kaski, D., Anderson, T., & Hallett, M. (2022). Eye movement disorders in movement disorders. Movement Disorders Clinical Practice. https://doi.org/10.1002/mdc3.13413
Mukherjee, S., Sakunthala, A., Gadhe, L., Poudyal, M., Sawner, A. S., Kadu, P., & Maji, S. K. (2022). Liquid-liquid phase separation of α-synuclein: A new mechanistic insight for α-synuclein aggregation associated with Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Journal of Molecular Biology, 435(1), 167713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167713
Salvatore, M. F. (2024). Dopamine signaling in substantia nigra and its impact on locomotor function—Not a new concept, but neglected reality. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(2), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021131
Simonet, C., Tolosa, E., Camara, A., & Valldeoriola, F. (2019). Emergencies and critical issues in Parkinson’s disease. Practical Neurology, 20(1), practneurol-2018-002075. https://doi.org/10.1136/practneurol-2018-002075
Best Professors To Choose From For NURS 6501 Class
- Dr. Mary Smith
- Dr. Tara Harris
- Dr. Mahaman Moussa
- Dr. Annaliza (Anna Liza) Villena
- Dr. Morgan Skinner
(FAQs) related to NURS 6501 Week 7 Assignment
Question 1: Where can I download a free sample for NURS 6501 Week 7 Assignment?
Answer 1: Download a free sample from Tutors Academy.
Question 2: Where can I find the rubrics and instruction file for NURS 6501 Week 7 Assignment?
Answer 2: Get the rubric and instruction file from the Tutors Academy website.
Do you need a tutor to help with this paper for you with in 24 hours.
- 0% Plagiarised
- 0% AI
- Distinguish grades guarantee
- 24 hour delivery

