NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment FREE DOWNLOAD
NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment
Nursing Informatics Project
Student Name
Walden University
NURS 8210: Transforming Nursing and Healthcare Through Technology
Professor Name
Date
Slide 1:
Good morning, everyone. Today, I will present a proposed nursing informatics project designed for my healthcare organization.
Slide 2:
Introduction
Nursing informatics: bridging nursing practice and technology.
Aim: propose an informatics project for improved patient outcomes Guided by project management tools (SWOT, Gap, WBS, RACI, etc.)
Focus: design, scope, and implementation in healthcare setting.
Nursing informatics integrates clinical practice with technology to enhance patient safety, efficiency, and evidence-based decision-making. The aim of this project is to demonstrate how a structured informatics initiative can strengthen nursing practice while aligning with organizational goals. Throughout this presentation, I will apply project management tools and strategies, including SWOT analysis, Gap analysis, Work Breakdown Structure, and RACI charts.
Each of these will help us evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges of the proposed project. Furthermore, these methods will clarify the project scope, define responsibilities, and set timelines, ensuring a systematic approach (Harerimana et al., 2020). The presentation will begin with identifying the conversation held with a nurse leader, followed by project scope and charter documents. Then, I will walk you through the SWOT and Gap analyses, outline project deliverables through the WBS and Gantt chart, and review the communication and risk management plans.
Slide 3:
Nurse Leader Conversation & Scope
Discussion with nurse leader: project feasibility & organizational alignment
Key input: scope definition and resource needs
Charter outlines project purpose, objectives, stakeholders
Ensures leadership support and role clarity
To ensure this informatics project is both relevant and achievable, I initiated a conversation with a nurse leader in my healthcare organization. The discussion focused on identifying current challenges in nursing practice and determining how technology could address gaps in workflow and patient care. The nurse leader emphasized the importance of aligning the project with organizational priorities, such as patient safety, quality improvement, and efficient documentation. From this discussion, the need for clear scope and charter documents became evident (Moon et al., 2022).
The project scope document defines what the project will and will not cover. For example, the scope may include integrating an electronic clinical decision support tool into the electronic health record but exclude large-scale IT infrastructure changes. Clearly outlining these boundaries ensures that resources are used effectively and expectations are realistic. The project charter serves as the foundation of the project. It describes the purpose, measurable objectives, stakeholders, roles, and expected deliverables.
It also highlights the support from nursing leadership and interdisciplinary teams, which is critical for gaining buy-in. Together, the scope and charter documents ensure that the project remains focused, aligned with strategic goals, and positioned for successful implementation.
Slide 4:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths | Weaknesses |
– Enhances patient safety through evidence-based decision support | – Initial resistance from staff due to workflow changes |
Opportunities | Threats |
– Potential to expand into other units/departments | – Budget constraints may limit full implementation |
The SWOT analysis highlights the internal and external factors that can influence the success of the proposed nursing informatics project.
Strengths include the project’s direct impact on patient safety and alignment with the organization’s vision of digital transformation. By embedding evidence-based tools within the electronic health record (EHR), nurses can make quicker, more informed decisions while reducing documentation burden. However, weaknesses also exist.
Staff may initially resist change due to disrupted workflows, and the project requires both training and consistent IT support. Additionally, older EHR systems may pose challenges for seamless integration. Looking at opportunities, the project can be scaled across multiple units once proven effective in the pilot phase. It also strengthens compliance with regulatory requirements for quality reporting and promotes interdisciplinary collaboration by ensuring all stakeholders access the same accurate data.
Finally, threats must be acknowledged. Budget limitations and financial constraints could affect implementation. Vendor dependency may lead to project delays, while cybersecurity threats continue to pose significant risks to patient data privacy. Overall, this SWOT analysis underscores the importance of strategic planning and proactive risk management to leverage strengths and opportunities while minimizing weaknesses and threats.
Slide 5:
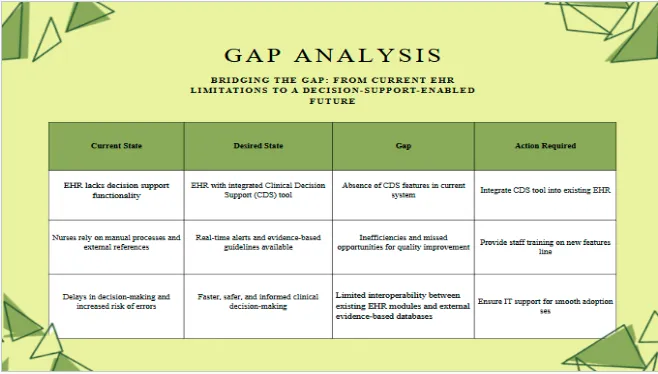
The Gap Analysis Map illustrates the difference between where our organization currently stands and where we need to be to optimize nursing practice through informatics.
In the current state, our EHR lacks advanced decision support capabilities. Nurses frequently rely on manual references and external resources, which slows down clinical decision-making and can increase the risk of errors. This limited functionality contributes to inefficiencies and adds to the workload of already overburdened staff. The desired state envisions a fully integrated Clinical Decision Support (CDS) tool embedded within the EHR.
This system would provide real-time alerts, prompts, and evidence-based guidelines directly at the point of care. By doing so, nurses can make faster, safer, and more informed decisions, ultimately improving patient outcomes and aligning with organizational goals for quality improvement. The identified gaps are significant. First, the absence of CDS features creates a barrier to safe and efficient practice.
Second, inefficiencies and missed opportunities for quality improvement continue to affect patient care. Third, limited interoperability between the EHR and external databases restricts timely access to evidence-based resources. The action plan to bridge this gap includes integrating the CDS tool, ensuring interoperability, and providing comprehensive staff training supported by IT resources.
Slide 6:
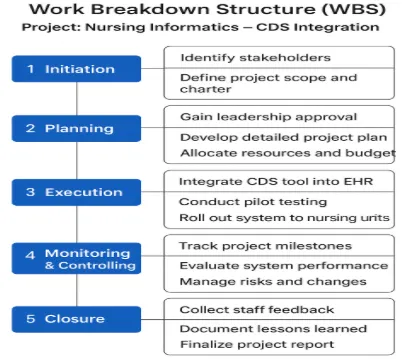
This slide presents the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) for our Nursing Informatics project, which focuses on integrating a Clinical Decision Support (CDS) tool into the Electronic Health Record (EHR). The WBS provides a roadmap by breaking the project into manageable phases and deliverables, ensuring we remain organized and aligned with our objectives (Alexiuk et al., 2023). We begin with the initiation phase, where we identify key stakeholders such as nurses, IT staff, physicians, and leadership, define the project scope, and create a project charter that outlines our goals, boundaries, and success measures.
This phase concludes with gaining leadership approval to formally launch the project. Moving into the planning phase, a detailed project plan is developed that defines timelines and deliverables. Resources and budget are allocated to cover technology, training, and support, while a comprehensive training strategy is designed to prepare nursing staff and clinicians for effective adoption of the CDS system. In the execution phase, the CDS tool is integrated into the EHR, beginning with pilot testing in a smaller environment to identify and resolve issues, followed by a full rollout across all relevant units.
The monitoring and controlling phase involves tracking milestones, evaluating system performance, and managing risks or changes to ensure that the project remains on track and continues to meet its objectives. Finally, in the closure phase, staff feedback is gathered to assess user experience and the system’s overall impact, lessons learned are documented for future reference, and a final project report is prepared for leadership and stakeholders. Overall, this WBS provides a structured approach that ensures every stage of the CDS integration is clear, accountable, and focused on achieving successful outcomes.
Slide 7:
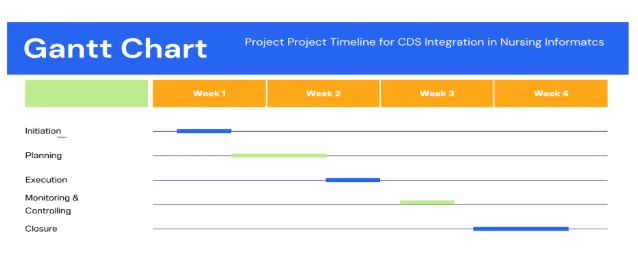
Project Timeline – CDS Integration
This slide illustrates the project timeline for the Nursing Informatics CDS integration. We begin with initiation during the first two weeks, focusing on stakeholder identification, scope definition, and project approval. Planning follows in weeks three to five, where we finalize detailed project activities, resource allocation, and training strategies. Execution, which is the longest phase, runs from weeks six through twelve and includes CDS integration, pilot testing, and system rollout across units.
Alongside execution, we also conduct monitoring and controlling from week six through week fourteen to ensure progress is tracked, risks are managed, and system performance is evaluated continuously (Zhai et al., 2022). Finally, the closure phase in weeks fifteen and sixteen involves collecting feedback, documenting lessons learned, and preparing the final project report. The timeline helps align the team on when key activities will occur and ensures that deadlines are both realistic and achievable.
Slide 8:
RACI Chart – CDS Integration Project
Task/Phase | Responsible (R) | Accountable (A) | Consulted (C) | Informed (I) |
Identify stakeholders | Project Manager | Nursing Director | Clinical Leads, IT Team | Nursing Staff |
Develop project plan | Project Manager | Nursing Director | IT Manager, Finance | Unit Managers |
System integration (EHR + CDS) | IT Team | IT Manager | Vendor, Nurses | Leadership |
Staff training | Nurse Educators | Nursing Director | IT Support, Unit Managers | All Nursing Staff |
Pilot testing | IT Team, Nurses | Project Manager | Vendor, Clinical Leads | Leadership, Staff |
System rollout | Project Manager | Nursing Director | IT Team, Unit Managers | All Stakeholders |
Monitoring & evaluation | Quality Officer | Nursing Director | Project Manager, IT Team | Leadership, Staff |
This slide presents the RACI chart for the CDS integration project, which clarifies roles and responsibilities across the team. For each project activity, the chart identifies who is responsible for completing the task, who is accountable for final decisions, who must be consulted for their expertise, and who needs to be kept informed. For example, the project manager is primarily responsible for stakeholder identification and project planning, while the nursing director remains accountable for ensuring alignment with organizational goals. The IT team takes responsibility for system integration, with the IT manager accountable, and vendors and nurses consulted to ensure smooth functionality.
Staff training is led by nurse educators, supported by IT, with all nurses informed. Pilot testing and system rollout involve collaboration between the IT team, nurses, and unit managers, with leadership kept updated throughout (Altmiller & Pepe, 2022). Monitoring and evaluation are overseen by the quality officer to ensure the project meets regulatory and clinical standards. Finally, project closure and reporting are led by the project manager, with input from clinical leads and finance. This RACI chart ensures clarity, accountability, and effective communication across the project team.
Slide 9:
Communication Plan
Audience | Information to Share | Frequency | Channel/Method |
Nursing Staff | Training updates, workflow changes | Weekly | Emails, Staff Meetings |
IT Team | Technical progress, integration issues | Twice Weekly | Project Management Tool, Calls |
Nursing Director | Milestones, budget updates | Bi-weekly | Reports, Briefings |
Clinical Leads | Pilot testing feedback, system updates | Weekly | Meetings, Shared Dashboard |
Leadership/Executives | Project status, risks, outcomes | Monthly | Executive Reports, Presentations |
Patients (Indirect) | Benefits of CDS, safety improvements | At Implementation | Posters, Informational Leaflets |
Slide 10:
Risk Management Plan
Risk | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
Staff resistance to workflow changes | Delays adoption, reduced effectiveness | Early engagement, training, change champions |
Integration issues with legacy EHR systems | Disruptions, reduced functionality | Pilot testing, phased rollout, IT support |
Budget overruns | Project delays or scope reduction | Careful planning, contingency funds, regular budget review |
Cybersecurity & data privacy concerns | Data breaches, legal non-compliance | Robust encryption, compliance (HIPAA/GDPR), monitoring |
Vendor dependency delays | Missed deadlines, extended rollout | Strong vendor contracts, alternative support arrangements |
This slide presents the risk management plan for the CDS integration project. One of the most significant risks is staff resistance to workflow changes, which could delay adoption and reduce system effectiveness. To mitigate this, we will provide early training, engage staff in the planning process, and identify change champions to support peers. Technical risks also exist, particularly integration issues with legacy EHR systems, which may cause disruptions.
These will be addressed through pilot testing, phased rollouts, and continuous IT support. Budget overruns pose another challenge, so we will implement careful financial planning, set aside contingency funds, and conduct regular budget reviews (Pooya Rostami Mazrae et al., 2023).
Cybersecurity and data privacy are also major concerns, given the sensitive nature of patient information. To mitigate this, robust encryption methods, compliance with HIPAA and GDPR, and active monitoring will be enforced. Finally, vendor dependency could cause delays, so clear contracts and alternative support arrangements will be established. This structured risk management plan ensures that potential threats are identified early and addressed effectively to safeguard the success of the project.
Rationale
Why this project matters
Language barriers reduce productivity and exclude participants.
What the literature says
Accessibility: Enhances inclusivity for diverse language users.
Productivity: Reduces delays, improves collaboration.
Technology trends: AI and NLP widely adopted in communication tools.
Case studies: Translation tools improve cross-border teamwork and client relations.
Connection to project
Supports AI-powered translation for Zoom as a solution to communication challenges.
On this slide, I will explain the rationale behind the project using scholarly literature.
First, research shows why this project is important—language barriers in online meetings often lead to misunderstandings, reduced productivity, and even exclusion of participants. Second, scholars emphasize that real-time translation tools improve accessibility, making virtual meetings more inclusive for participants with different language backgrounds. They also highlight that such tools boost productivity by minimizing delays and improving teamwork.
Third, technology trends show that AI and Natural Language Processing are becoming standard features in business communication platforms, which means our project is aligned with the direction of global innovation.
Finally, case studies demonstrate that companies already using translation tools in video conferencing have reported stronger cross-border collaboration and better client relationships. Altogether, this literature confirms that our project—an AI-powered real-time translation feature for Zoom—is both necessary and valuable, as it addresses current challenges and provides practical benefits.
Slide 11:
Conclusion
- Real-time translation addresses critical language barriers in online meetings.
- Enhances accessibility, productivity, and global collaboration.
- Supported by scholarly literature and industry case studies.
- Aligns with AI and NLP technology trends in communication.
- Project contributes to inclusive, efficient, and future-ready virtual interactions.
In conclusion, this project shows that integrating real-time language translation into Zoom is both practical and impactful.
We’ve seen that language barriers are a major obstacle in virtual communication, leading to misunderstandings and lower productivity. Our proposed solution directly addresses these challenges. The literature consistently highlights three key benefits: improved accessibility, where all participants can engage regardless of language; greater productivity, by reducing delays and confusion; and enhanced global collaboration, as teams from different regions can work seamlessly together.
Case studies and industry trends confirm that AI and NLP are rapidly becoming standard tools in business communication, meaning this project is well-timed and highly relevant. Ultimately, this project will not only make Zoom meetings more inclusive and efficient, but also help organizations adapt to the future of digital communication.
Instructions To Write NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment
Need instructions for this assessment? Contact us now and get expert guidance right away!
Instructions File For 8210 Week 6 Assignment
DESIGNING A NURSING INFORMATICS
PROJECT FOR YOUR ORGANIZATION
You will use project management tools and strategies to propose how you would support and potentially implement a nursing informatics project. While you may not have the opportunity to implement this proposed project, this project will allow you to apply the skills needed and the considerations that are required in deducing how a project of this scope might take place in your nursing practice.To complete this project, you will define a informatics project that would be beneficial to your healthcare organization or nursing practice. You can discuss this with upper leadership, in your practice or organization, explaining that you will need to design is proposed informatics
RESOURCES
Be sure to review the Learning Resources before completing this activity.
Click the weekly resources link to access the resources.
WEEKLY RESOURCES
THE ASSIGNMENT:10-11 SLIDES
This week, you will finalize your proposed Informatics Project, using all work completed during Weeks 1–5. Be sure that each table or figure is explained with a short text description just before you include the table or figure in your presentation (APA 7).
Introduction
Identify and initiate a conversation with a nurse leader at your nursing practice or healthcare organization. Discuss what you will need to develop Scope and Charter Documents.
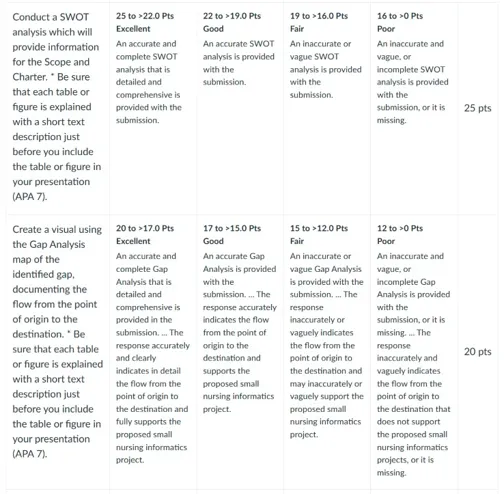
Conduct a SWOT analysis which will provide information for the Scope and Charter. You can use a Word document and insert a table. Directions can be viewed in the Week 3 media piece, How to Perform a SWOT Analysis , found in this week’s Learning Resources. Some of the content is relevant to both the project for this course as well as organization of your doctoral dissertation. Overall, the first step for any project, work or your dissertation, requires a plan: what you will and will not do. That information is defined in a charter and scope.
Create a visual using the Gap Analysis map of the identified gap, documenting the flow from the point of origin to the destination. After watching the Week 3 media piece, How to do a GAP Analysis , identify the gap and analyze the flow or lack of flow of information as the gap in a process. The visual map will include the flow from the point of origin to the destination.
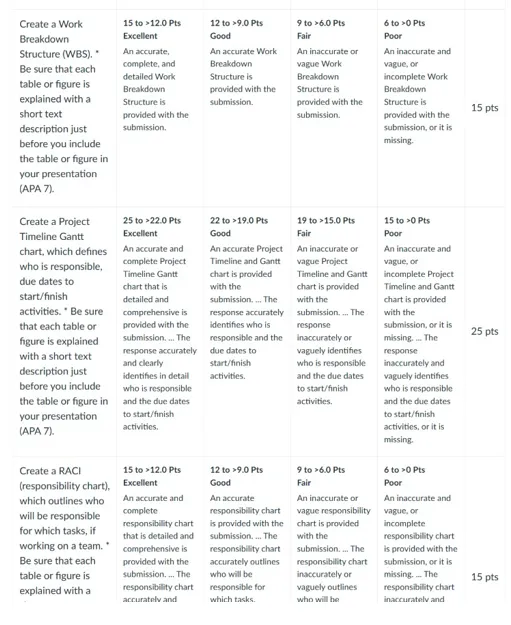
Create a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) using PowerPoint slides or another method. Be sure to review the media piece, What Is a Work Breakdown Structure? In the Week 3 Learning Resources.
Create a Project Timeline Gantt chart, which defines who is responsible, due dates to start /finish activities. Be sure to review the Gantt Charts, Simplified media piece in this week’s Learning Resources.
Lavallee, L. (2023). The importance of a communication plan in project management ⏱️.
https://www.sinhu.edu/about-us/newsroom/business/communication-plan-in-project-management
RACI (responsibility chart) which outlines who will be responsible for which tasks, if working with a team.
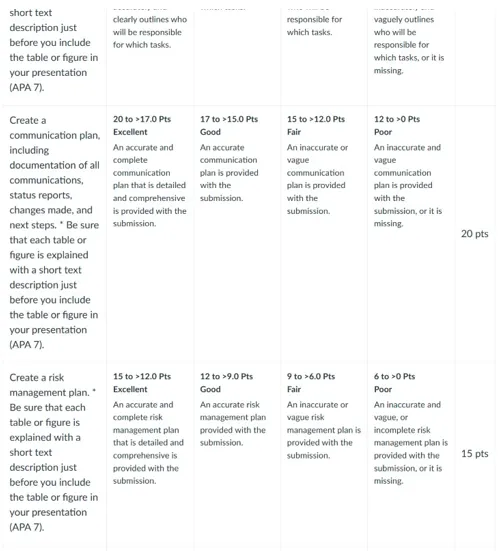
Communication plan – include documentation of all communications, status reports, changes made, and next steps, especially if others will be responsible for helping you acquire documents such as IRB site documents if applicable.
Examples can be found in the Learning Resources, Required Readings.
Risk management plan– After viewing the “Risk Analysis How to Analyze Risks on Your Project” media piece in this week’s Learning Resources, document current and potential risks and how risks may be mitigated if possible.
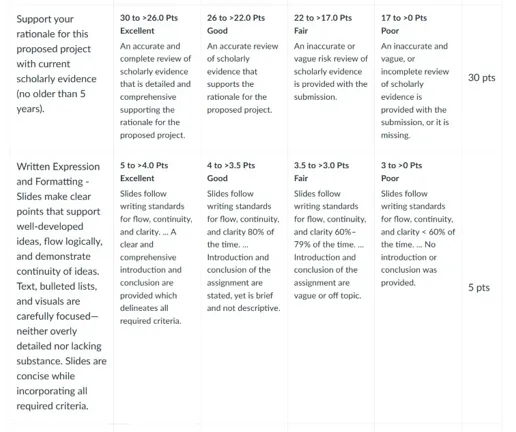
Rationale – Synthesize scholarly literature that supports your proposed project.
Conclusion
Reminder: The Sample Presentation Template is found in Week 6 Learning Resources. All presentations submitted must use this formatting.
Submit your Assignment by Day 7 of Week 6.
SUBMISSION INFORMATION
Before submitting your final assignment, you can check your draft for authenticity. To check your draft,
access the Turnitin Drafts from the Start Here area.
1.To submit your completed assignment, save your Assignment as WK6AssgnLastName.Firstinitial
2.Then, click on Start Assignment near the top of the page.
3.Next, click on Upload File and select Submit Assignment for review
NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment Rubrics
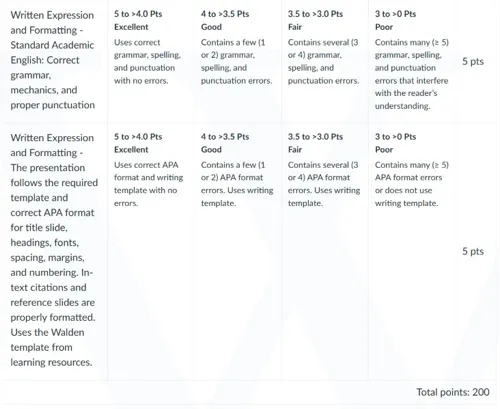
References For NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment
Alexiuk, M., Elgubtan, H., & Tangri, N. (2023). Clinical decision support tools in the EMR. Kidney International Reports, 9(1), 29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2023.10.019
Altmiller, G., & Pepe, L. H. (2022). Influence of Technology in Supporting Quality and Safety in Nursing Education. Nursing Clinics of North America, 57(4), 551–562.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnur.2022.06.005
Harerimana, A., Wicking, K., Biedermann, N., & Yates, K. (2020). Integrating nursing informatics into undergraduate nursing education in Africa: A scoping review. International Nursing Review, 68(3). https://doi.org/10.1111/inr.12618
Laka, M., Carter, D., Milazzo, A., & Merlin, T. (2022). Challenges and opportunities in implementing clinical decision support systems (CDSS) at scale: Interviews with Australian policymakers. Health Policy and Technology, 11(3), 100652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hlpt.2022.100652
Moon, S. E. J., Hogden, A., & Eljiz, K. (2022). Sustaining improvement of hospital-wide initiative for patient safety and quality: a systematic scoping review. BMJ Open Quality, 11(4), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjoq-2022-002057
Pooya Rostami Mazrae, Mens, T., Mehdi Golzadeh, & Decan, A. (2023). On the usage, co-usage and migration of CI/CD tools: A qualitative analysis. Empirical Software Engineering, 28(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10664-022-10285-5
Zhai, Y., Yu, Z., Zhang, Q., Qin, W., Yang, C., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Transition to a New Nursing Information System Embedded with Clinical Decision support: a mixed-method Study Using the HOT-fit Framework. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 22(1), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-022-02041-y
Best Professors To Choose From For 8210 Class
- Dr. David Sharp
- Donna W. Bailey
- Wendy R. Ostendorf
- Dr. Deborah Lewis
- Dr. Carolyn Sipes
(FAQs) related to NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment
Question 1: Where can I download a free sample for NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment?
Answer 1: Download a free NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment sample from Tutors Academy for expert guidance and project reference.
Question 2: Where can I find the rubrics and instruction file for NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment?
Answer 2: Get the complete rubrics and instructions for NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment at Tutors Academy for accurate formatting and grading help.
Question 3: What is NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment about?
Answer 3: The NURS 8210 Week 6 Assignment is a Nursing Informatics Project focused on using technology to improve patient outcomes and care efficiency.
Do you need a tutor to help with this paper for you with in 24 hours.
- 0% Plagiarised
- 0% AI
- Distinguish grades guarantee
- 24 hour delivery