NURS 6052 Module 2 Assignment FREE DOWNLOAD
NURS 6052 Module 2 Assignment
Evidence-Based Project, Part 1: Identifying Research Methodologies
Student Name
Walden University
NURS 6052: Essentials of Evidence-Based Practice
Professor Name
Date
Matrix Worksheet Template
Medication Administration Errors in Nursing Practice
Use this document to complete Part 1 of the Module 2 Assessment, Evidence-Based Project, Part 1: Identifying Research Methodologies.
Full citation of the selected article | Article #1 | Article #2 | Article #3 | Article #4 |
Tsegaye, D., Alem, G., Tessema, Z., & Alebachew, W. (2020). Medication administration errors and associated factors among nurses. International Journal of General Medicine, 13(13), 1621–1632. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijgm.s289452
| Brabcová, I., Hajduchová, H., Tóthová, V., Chloubová, I., Červený, M., Prokešová, R., Malý, J., Vlček, J., Doseděl, M., Malá-Ládová, K., Tesař, O., & O’Hara, S. (2023). Reasons for medication administration errors, barriers to reporting them and the number of reported medication administration errors from the perspective of nurses: A cross-sectional survey. Nurse Education in Practice, 70(1), 103642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2023.103642 |
Moustafa Fathy, A. S., Shaaban Khalil, N., & Mohamed Taha, N. (2020). Nurse’s knowledge and Practice regarding Medication Errors in Critical Care Units: Descriptive study. Minia Scientific Nursing Journal, 008(1), 111–120. https://doi.org/10.21608/msnj.2020.188051 |
Afaya, A., Konlan, K. D., & Kim Do, H. (2021). Improving patient safety through identifying barriers to reporting medication administration errors among nurses: An integrative review. BMC Health Services Research, 21(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-07187-5 | |
Why you chose this article and/or how it relates to the clinical issue of interest (include a brief explanation of the ethics of research related to your clinical issue of interest) | I selected the article since it specifically focuses on medication administration errors (MAEs), which is an urgent issue in the field of patient safety and clinical practice. MAEs may cause patient harm, additional health expenditures, longer hospitalization, and even death. Identifying the factors that contribute to it, including ineffective communication, training deficiencies, and interruption, can assist in designing specific interventions that would enhance nursing practice and minimize errors. Ethically, studies of MAEs should guarantee confidentiality and non-punitive analysis of mistakes. It means that nurses involved in such research will be able to report errors without fear of punishment, which is in line with ethical principles of beneficence, non-maleficence, justice, and respect to persons. The ethical rigor in this study includes the fact that the questionnaires are anonymous and the study includes checklists of observation, which limits the bias and ensures that the identity of the participants is not revealed. | I chose this article since it broadens the scope of MAEs by going beyond identification of causes to also examine barriers to reporting as a critical but underrecognized area of medication safety. The knowledge of the reasons why nurses might be reluctant to report errors, e.g. the fear of being blamed or facing legal implications, allows one to have a more holistic picture of the systemic and psychological issues of improving medication safety. On the ethical side, the article mentions the necessity of a just culture in healthcare, where the focus is on transparency and learning instead of punishing. It promotes ethical nursing care through the advocacy of non-punitive reporting systems and lifelong learning, making sure that the safety of the patients and the well-being of nurses are both taken into consideration. | I chose the article as it specifically addresses the topic of knowledge and practice of nurses related to medication administration errors in critical care units, where patients are the most susceptible to injury due to these errors. This attention is of great concern to such a clinical problem as patient safety and the prevention of medication errors, in particular, in high-risk settings. The results highlight the areas of knowledge deficit and unsafe practices that should be eliminated to promote the best quality of care. | I selected the article since it explores a very important aspect of the larger clinical problem of medication administration errors (MAEs): the obstacles to reporting MAEs. A culture of fear, lack of clarity, and punitive systems can make nurses fail to report errors, even when they do occur making it hard to take corrective measures. The article fits the current trend in the healthcare sector toward promoting transparency, safety, and relentless improvement. Ethically, the article reaffirms the value of non-punitive reporting programs, which align with ethical principles of justice, accountability, and patient advocacy. By establishing a culture where reporting errors is not feared, one will facilitate mistake proof learning and adherence to the ethical responsibility of healthcare workers to ensure patient safety comes first. |
Brief description of the aims of the research of each peer-reviewed article | The overall objective of the research study was to determine the prevalence of medication administration errors (MAEs) among nurses in referral hospitals in Ethiopia. The researchers were interested in measuring the degree of occurrence of these errors in clinical practice and learn more about their effect on patient safety. The other objective was to establish the most prominent variables relating to MAEs, which included the absence of training, ineffective communication, interruptions, and the inaccessibility of guidelines. Identifying these sources of influence, the research aimed to inform future interventions and policy-making efforts in minimizing the MAEs and enhancing the quality of nursing care. | This study was conducted to discover the reasons behind the medication administration errors (MAEs), as well as to characterize the obstacles to reporting those errors, and finally to determine the rate, at which those errors are reported by the nurses in practice. By studying these aspects, the researchers were willing to enhance the current understanding of MAEs and indicate the areas that should be changed in nursing practice and hospital policy. The study also sought to determine the effect of demographic data, including age and years of clinical experience on the reporting and incidence of MAEs. The information will be used to guide the formulation of specific education and support mechanisms that look at the prevention and the honest reporting of medication errors. | The core objective of the research was to evaluate the knowledge and practices of nurses who are employed in critical care units regarding medication administration errors. Through the assessment of the knowledge and performance of nurses involved in medication administration, the study aims to identify the knowledge gaps that can potentially lead to patient harm and suggest effective interventions. Moreover, the research question was whether there was any relationship between demographic features (age, experience, or level of education) and differences in knowledge and practice. The results, that showed insignificance of demographic differences, imply that the knowledge gaps are systematic and prevalent, indicating the necessity of educational reforms on an institutional level. | The primary purpose of this integrative review was to syntactically determine and analyze the obstacles hindering nurses from reporting medication administration errors within hospital facilities. The research advocates the significance of error reporting to accomplish the objectives of the WHO 2017 challenge to decrease medication-related harm in all parts of the world. The authors aimed to synthesize the evidence of numerous studies to categorize the themes of such barriers, both organizational and individual, to propose changes in policy, culture, and education that would contribute to error reporting and improve patient safety. |
Brief description of the research methodology used Be sure to identify if the methodology used was qualitative, quantitative, or a mixed-methods approach. Be specific. | The research design was quantitative, institutional-based, cross-sectional; 422 nurses were involved in the research, and they were selected with the help of simple random sampling. The instruments used in data collection were a semi-structured self-administered questionnaire and an observational checklist which had been pre-tested to ensure accuracy and consistency. The researchers summarized the characteristics of participants and error types with the help of descriptive statistics and then determined statistically significant factors related to MAEs through binary logistic regression. The significance of the associations was defined by the use of p-value = 0.05 or below and thus, the results are statistically well-grounded and oriented towards the quantifiable outcomes. | The design used by the researchers in this study was quantitative, descriptive, and cross-sectional. The tool used to acquire the data was the standardized Medication Administration Error Survey, which was given to 1,205 nurses employed in Czech Republic hospitals, which made the study sociologically representative. Descriptive statistics were applied to sum up the frequency and causes of MAEs, and Pearson correlation and Chi-square Automatic Interaction Detection were applied to examine relations among variables. This powerful statistical method allowed the authors to make relevant conclusions regarding errors and underreporting patterns and predictors. | A descriptive exploratory design was used by the researchers to carry out this study. A convenience sample of 60 nurses working in different critical care units (e.g., ICU, cardiac care, stroke unit) at Al Minia University Hospital was taken, and two structured tools were used to collect the data: a questionnaire to gain demographic and knowledge information and a checklist to evaluate the practical medication administration skills. It is a quantitative methodology; that is, it deals with numerical ratings of knowledge and practice. It enabled researchers to quantify and juxtapose the degree of knowledge and proficiency amid nurses. Although the study sample was small, the structured methodology of the study gave some preliminary data on what could be a very important issue in critical care nursing. | The methodology of the present article was an integrative review, which enabled the researchers to synthesize the results of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods studies published between 2016 and 2020. The articles located in the databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, CINAHL, and Google Scholar, were included in the review. After the rigorous screening and quality assessment with the aid of the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) 2018, 14 high-quality studies were incorporated. This approach allowed the authors to thoroughly investigate statistical patterns and lived experiences on obstacles to error reporting. |
A brief description of the strengths of each of the research methodologies used, including reliability and validity of how the methodology was applied in each of the peer-reviewed articles you selected. | Among the key strengths of the research methodology, the fact that it relied on a large sample size (414 participants) and a high response rate (98.1 percent) deserves to be mentioned first because it enhances the reliability and external validity of the results. Also, a questionnaire combined with an observational checklist is multilayered since it provides an opportunity to triangulate the data, and the chance of self-report bias is low. Methodology also exhibited high validity with the tools used being pre-tested to establish that they were clear and relevant to the study population. Binary logistic regression analysis was a strong point of the analysis as it enabled the determination of the independent predictors of MAEs, thus, more precise conclusions could be drawn, and the evidence-based practice could be improved. | The significant strength of this study was its large and varied sample size, comprising more than a thousand nurses working in various institutions, which enhanced the trustworthiness and applicability of the results. Internal validity was further contributed by the fact that a standardized survey instrument was used to ascertain uniformity in the collection of data among the various participants. To make the analysis stronger, the multiple statistical approaches were used to identify the complex relationships and interaction between the variables, such as Pearson, and CHAID. Moreover, the use of the STROBE statement promoted the transparency and the rigor of the research process, which supports the credibility and applicability of the findings to the actual nursing practice. | Among the strengths of the methodology, the dual approach with the questionnaire and practice checklist may be noted, as it makes it possible to assess the competence of nurses more fully, including what they know and how they do it. This assists in establishing the discrepancies between theory and practice, which is critical in specific education. Also, structured and validated tools increase the reliability of the results, whereas implementation of the study across several critical care environments increases its relevance to a variety of clinical practices. Although generalizability is compromised by the convenience sample, the study gives a good basis to future researches and interventions on a bigger scale. | Among the key advantages of this integrative review is that it is thorough and methodical in the collection of data in terms of the various methodologies and sources. The review provides a comprehensive picture of the multifaceted nature of the reasons why nurses are hesitant to report MAEs because it included both qualitative and quantitative data. Also, the quality of included studies measured with the help of the MMAT tool makes the research credible and reliable. This enhances the credibility of the conclusions and recommendations, which can be of use in informing the practice and policy enhancement in healthcare organizations across the world. |
General Notes/Comments |
Instructions To Write NURS 6052 Module 2 Assignment
Need instructions for this assessment? Contact us now and get expert guidance right away!
Instructions File For 6052 Module 2 Assignment
EVIDENCE-BASED PROJECT, PART 1:
IDENTIFYING RESEARCH METHODOLOGIES
Is there a difference between “common practice” and “best practice”?
When you first went to work for your current organization, experienced colleagues may have shared with you details about processes and procedures. Perhaps you even attended an orientation session to brief you on these matters. As a “rookie,” you likely kept the nature of your questions to those with answers that would best help you perform your new role.
Over time and with experience, perhaps you recognized aspects of these processes and procedures that you wanted to question further. This is the realm of clinical inquiry.
Clinical inquiry is the practice of asking questions about clinical practice. To continuously improve patient care, all nurses should consistently use clinical inquiry to question why they are doing something the way they are doing it. Do they know why it is done this way, or it is just because we have always done it this way? Is it a common practice or a best practice?
In this Assignment, you will identify clinical areas of interest and inquiry and practice searching for research in support of maintaining or changing these practices. You will also analyze this research to compare research methodologies employed.
RESOURCES
Be sure to review the Learning Resources before completing this activity.
Click the weekly resources link to access the resources.
WEEKLY RESOURCES
To Prepare:
Review the Resources and Identify a clinical issue of interest that can form the basis of a clinical inquiry. Keep in mind that the clinical issue you identify for your research will stay the same for the entire course.
Based on the clinical issue of interest and using keywords related to the clinical issue of interest, search at least four different databases in the Waldem Library to identify at least four relevant peer-reviewed articles related to your clinical issue of interest. You should not be using systematic reviews for this assignment, select original research articles.
Review the results of your peer-reviewed research and reflect on the process of using an unfiltered database to search for peer-reviewed research.
Reflect on the types of research methodologies contained in the four relevant peer-reviewed articles you selected.
Part 1: Identifying Research Methodologies
After reading each of the four peer-reviewed articles you selected, use the Matrix Worksheet template to analyze the methodologies applied in each of the four peer-reviewed articles. Your analysis should include the following:
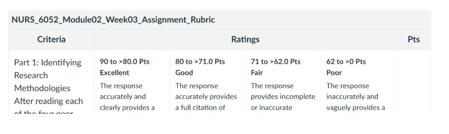
The full citation of each peer-reviewed article in APA format.
A brief (1-2 paragraph) document explaining why you chose this peer-reviewed article and/or how it relates to your clinical issue of interest, including a brief explanation of the ethics of research related to your clinical issue of interest.
A brief (1-2 paragraph) description of the aims of the research of each peer-reviewed article.
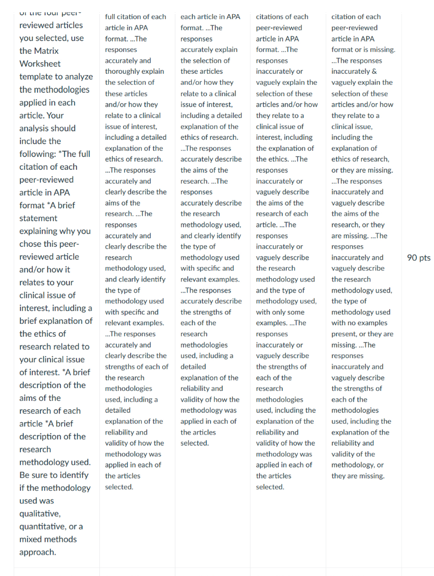
A brief (1-2 paragraph) description of the research methodology used. Be sure to identify if the methodology used was qualitative, quantitative, or a mixed-methods approach. Be specific.
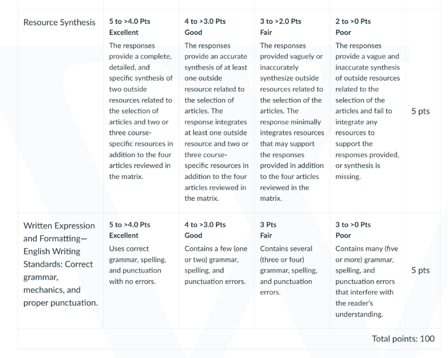
A brief (1- to 2 paragraph) description of the strengths of each of the research methodologies used, including reliability and validity of how the methodology was applied in each of the peer-reviewed articles you selected.
BY DAY 7 OF WEEK 3
Submit your Evidence-Based Project.
SUBMISSION INFORMATION
Before submitting your final assignment, you can check your draft for authenticity. To check your draft, access the Turnitin Drafts from the Start Here area.
To submit your completed assignment, save your Assignment as MD2Assgn+last name+first initial
Then, click on Start Assignment near the top of the page.
Next, click on Upload File and select Submit Assignment for review.
6052 Module 2 Assignment Rubrics
References For NURS 6052 Module 2 Assignment
Afaya, A., Konlan, K. D., & Kim Do, H. (2021). Improving patient safety through identifying barriers to reporting medication administration errors among nurses: An integrative review. BMC Health Services Research, 21(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-07187-5
Brabcová, I., Hajduchová, H., Tóthová, V., Chloubová, I., Červený, M., Prokešová, R., Malý, J., Vlček, J., Doseděl, M., Malá-Ládová, K., Tesař, O., & O’Hara, S. (2023). Reasons for medication administration errors, barriers to reporting them and the number of reported medication administration errors from the perspective of nurses: A cross-sectional survey. Nurse Education in Practice, 70(1), 103642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2023.103642
Moustafa Fathy, A. S., Shaaban Khalil, N., & Mohamed Taha, N. (2020). Nurse’s knowledge and practice regarding medication errors in critical care units: Descriptive study. Minia Scientific Nursing Journal, 008(1), 111–120. https://doi.org/10.21608/msnj.2020.188051
Tsegaye, D., Alem, G., Tessema, Z., & Alebachew, W. (2020). Medication administration errors and associated factors among nurses. International Journal of General Medicine, 13(13), 1621–1632. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijgm.s289452
Best Professors To Choose From For NURS 6052 Class
- Dr. Donna Hathorn
- Dr. Judith (Judy) Cornelius
- Dr. Danielle Beasley
- Dr. Usama Saleh
- Dr. Wendy Ostendorf
(FAQs) related to NURS 6052 Module 2 Assignment
Question 1: Where can I download a free sample for NURS 6052 Module 2 Assignment?
Answer 1: Download a free sample from Tutors Academy.
Question 2: Where can I find the rubrics and instruction file for NURS 6052 Module 2 Assignment?
Answer 2: Get the rubric and instruction file from the Tutors Academy website.
Do you need a tutor to help with this paper for you with in 24 hours.
- 0% Plagiarised
- 0% AI
- Distinguish grades guarantee
- 24 hour delivery

