NURS FPX 8022 Assessment 4 Sample FREE DOWNLOAD
NURS FPX 8022 Assessment 4 Quality Improvement Project Plan Using Informatics/Technology
Student name
NURS-FPX8022
Capella University
Professor Name
Submission Date
Quality Improvement Project Plan Using Informatics/Technology
Adopting a predictive analytics system using AI, embedded within the electronic health record (EHR) is a key quality improvement project at Massachusetts general hospital (MGH), as it will fill ongoing gaps in safety and coordination as manifested in current performance indicators. The facility currently has a Leapfrog Hospital Safety Grade of A and a troubling postoperative sepsis score of 4.69, which is why the project specifically focuses on preventing harm events that can be avoided, including sepsis, patient falls, and adverse drug reactions (Afolalu et al., 2024).
The predictive analytics project uses real-time data to identify when patients are deteriorating early, to reduce care delays and errors. Since effective implementation will lead to better clinical decision-making, better Medicare Compare scores, fewer adverse patient outcomes, and adherence to national safety standards and requirements, the initiative will be consistent with national healthcare quality standards and regulatory requirements.
Problem Significance and Impact
The issue at MGH that needs the most attention is safety risks and avoidable adverse events that endanger patients and lead to patient outcome gaps and system efficiency gaps. The present data shows a negative event score of 1.02 and a patient fall rate of 0.199, which also shows weak areas even with the good overall performance (Hidayati, 2024). Despite the EHR system at MGH being advanced and having both computerized physician order entry (CPOE) and clinical decision support (CDS), the current system does not provide predictive functions and real-time monitoring to anticipate safety threats (Luo et al., 2020). The technology gap is most evident in the inability to identify clinical deterioration in a timely manner, warn staff about the development of dangerous comorbidities such as sepsis, or actively prevent falls issues directly correlated with the prevalence of adverse events.
The importance of the issue is complex, as it directly impacts some of the main stakeholders, including executive leadership, clinical departments, information technology (IT) professionals, medical workers, legal compliance and legal teams, and so on. The CMS and other governmental oversight subject the executive staff to economic forces pressure that not being focused on carrying force could act conflict with such an organization through the reimbursement and image (Kruse et al., 2022).
The delay in the working process (which occurs together with poor-quality service) impacts the next clinical units: the critical care department, the surgery department, and the nursing department, in which the problem of the IT department falls within the integration context, the data reliability, and systems stability (Garcia et al., 2022). Bedside clinicians and medical staff rely on correct, timely information to make life-saving decisions, and present deficiencies in systems prevent early detection and response, adding to workload and moral distress. The legal advisors should guarantee that all practices are being operated responsibly in accordance with the landscapes of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and that there is no fixed pledge to avoid any breaches and miscommunication of data unless we engage in stricter and comprehensive control of the Internet.
Data to Support the Problem and Trigger a Need for a Practice Change
What the Leapfrog hospital safety grade data shows are certain patient safety performance problem areas at MGH that should be addressed immediately. The overall A rating of the facility suggests that there is a general compliance with safety, but some subcategories show dire gaps. Of most concern is the postoperative sepsis score of 4.69, which is very high compared to the national average and a very high risk to patient recovery (LeapFrog, n.d; Medicare Compare, 2024).
On the same note, the harmful events score of 1.02 and patient fall rate of 0.199 show that frequent safety lapses occur (LeapFrog, n.d.). The results indicate that, although EHR is strong, there are no early-detection tools, and still, most of the important safety processes are controlled by manual processes. In Leapfrog data, MGH has a good overall grade, but the grade continues to experience severe safety dilemmas, particularly postoperative sepsis and patient falls, which explains why technological solutions are extremely required to embrace data-driven care proactively.
Medicare Compare data has another confirmation of the quality gap. The MGH was rated with five stars in patient experience, four stars in timeliness of care, and three stars in safety of care, which led to a total rating of five stars (excellent but could be improved in safety). For comparison, the closest competitors, Boston Medical Enterprise and Tufts medical personnel, all had three stars for general performance; that is, MGH appeared to be a local leader for both outcomes and experience, not for everything; the danger occasions could be minimized, and safety indications could be eradicated (Medicare Compare, 2024).
Although MGH performs better than its local hospitals, the Medicare Compare data continue to reveal that there are performance differences associated with safety, especially adverse events and sepsis, which elucidates the pressing need to implement a predictive, AI-enhanced informatics intervention. The performance gaps directly influence reimbursement, public trust, and the capacity to provide high-reliability healthcare in a competitive clinical environment.
Technology/ Informatics Solution
The proposed solution is the introduction of an AI-based predictive analytics tool as an addition to the existing EHR system of the MGH organization. To avoid negative effects, such as sepsis, patient falls, and medication errors, the integration will use real-time information to prevent and predict negative effects. The areas of concern are as defined by Leapfrog and Medicare Compare data. The vision of MGH is to be a proactive patient-centered healthcare entity that is data-driven and forecasts risk prior to its occurrence, minimizes harm, and achieves high scores in the Leapfrog and the Medicare Compare performance rates (Mulac et al., 2021). The solution will integrate evidence-based clinical rules, predictive models, and individual clinical decision support systems, and will ensure that clinicians are well prepared to provide interventions at the right time and without error.
The technology upgrade will elevate MGH to a national leader in the use of advanced informatics in the context of patient care safety, personalization,n and efficiency. The integrated predictive system will also reduce clinical workflow through automatic processing of patient vitals, laboratory findings, and health history, and issue early notifications of clinical deterioration. The system will identify the sepsis and falls risk and prescribe evidence-based interventions in real-time when patients are admitted to the medical facility (Dixon et al., 2024).
The system will also include barcode medication administration, wearable monitoring, and patient portals that will support end-to-end patient status monitoring. The enhancements will directly respond to the weaknesses indicated in the postoperative sepsis score of 4.69, harmful event score of 1.02, and patient fall rate of 0.199 that have contributed to the increase in Leapfrog safety scores and Medicare Compare quality ratings (LeapFrog, n.d.; Medicare Compare, 2024). The workflow will be faster, which will result in fewer delays, enhanced resource utilization, and increased patient safety.
Data Points
Postoperative Sepsis Rate
The main data point will be the incidence of postoperative sepsis, which is an urgent Leapfrog metric. Current Leapfrog and EHR data will be used to get baseline measurements. The Leapfrog hospital safety grade dashboard (LeapFrog, n.d.) will be the monitoring tool. Thus, any quantifiable reduction in the score after the implementation will be a sign that predictive analytics is facilitating an earlier detection and intervention.
- Patient Fall Rate
The measure will be the inpatient falls per 1,000 patient days. The motion sensor and the AI-based risk scoring algorithms will alert those at-risk patients subscribed to the system (Alharbi et al., 2023). Live analytics will enable personnel to take timely action. Quarterly evaluations will be used to determine whether the 0.199 fall rate has been reduced, as reported in Leapfrog benchmarks, and modify fall prevention measures as necessary.
Adverse Drug Events (ADEs)
The third important data point will be adverse medication events. The surveillance will be based on ADEs and will be carried out via EHR-based computerized physician order entry (CPOE) and barcode readers (Calduch et al., 2021). Monthly error reports will be used to determine the error trend, and longitudinal analysis will be used to determine the improvement in prescription safety and staff compliance with alerts.
Implementation Plan
The proposed AI-based predictive analytics integration implementation plan will help to overcome safety and coordination gaps in MGH by focusing on preventable harm measures revealed by Leapfrog and Medicare Compare data analysis. The Fly-by implementation pathway, starting with the riskiest units (critical care and surgical), has the potential to minimize disruption and impact on performance while maximizing the impact as quickly as possible. The SAFER guidelines for assessment identified gaps with regard to EHR utilization, clinician burnout, and data security that will be addressed in the training and onboarding plan of all clinical staff (Sittig et al., 2025).
The emphasis of the plan on clinical engagement, technical support, and alignment for administrative actions represents an opportunity to induce change sustainably. One is directly related to the root causes of safety incidents, improved first notification, and automation of intervention protocols. With targeted metrics and embedded monitoring systems, the existing risks will not only be mitigated, but the informatics system created can provide resilience in the face of change to allow for ongoing quality improvement now and in the future.
Potential Implementation, Challenges, and Solutions
The main implementation issues are the resistance of personnel, the lack of interoperability of technologies, the risk of cybersecurity, and the shortage of resources. Personnel issues such as clinician burnout or reluctance to use new digital products, and fear of introducing more data entry, are also well-documented in the EHR literature (Kruse et al. 2022). When applying AI algorithms to the current EHR processes and introducing real-time monitoring with sensors, smart beds, and CDS alerts, logistical coordination challenges can occur.
Based on the risk mitigation plan developed above, the challenges may be addressed proactively using structured interventions. The issue of resistance to change will be discussed using the organizational change model of Kotter (1998), which emphasizes urgency, mobilization of a coalition, and frontline employee ownership of the change. The approach promotes confidence and reduces fear concerning emerging technologies.
Initial infrastructure, training, and maintenance requirements for the system are among the resource allocation considerations that are particularly relevant to smaller departments or satellite clinics (Alder, 2024). Strategies to address the challenge include phased funding, high-impact unit priorities, and administrative advocacy of capital investment. In order to achieve interdisciplinary alignment and minimize disruption of the workflow during implementation, the workflow redesign team will include IT professionals, nurse informaticists, physicians, and administrative leadership (Alami et al., 2022). With the implementation of predictive analytics, which will contribute to the clinical goals and improve patient safety and national performance indicators, MGH can successfully implement predictive analytics by overcoming such implementation challenges through strategic planning, training, and mitigation of risks based on risk education.
Leaders’ Role in Change Management
The deployment of the AI-based predictive analytics system in Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) is a leadership problem. Stakeholders: leadership of the health system, department heads, nurses, information technology (IT) leaders, and physician champions who need to synchronously engage for change to occur in the clinical and administrative world (Alami et al., 2022). The leaders need to provide the vision, enablement of interaction, coordination of dispersal of resources, and also need to abide by regulatory and ethical norms.
The leadership specifically matters since EHR integration is a complicated process, MGH is a huge organization, and it is necessary to align processes of various departments without any problem (Calduch et al., 2021). An effective communication plan should be developed to inform the stakeholders and motivate them through the change process. Multi-modal communication (email, meetings, dashboards, town halls) is expected to be adopted by managers based on the clinical, IT, and administrative personnel.
The positive outcomes of predictive analytics, such as the decrease in sepsis and falls, should be communicated openly, and the means of overcoming the fear of personnel that they will be overworked or that the technology will not work should also be addressed (Kruse et al., 2022). The most pragmatic way to bring about change is through the eight-step change process from Kotter, which looks at the big picture change and also echoes the urgency, empowerment, and consolidation of change.
We propose that the participation of clinicians at MGH can effectively address their resistance to the implementation of new technology burdens, and that our model can be applied to other clinical settings where the development of a sense of urgency, creating coalitions, and the achievement of short-term wins can be effective. The model capitalizes on the strengths of MGH, such as strong EHR infrastructure and strong clinical leadership, and the weaknesses, such as the unwillingness to change the workflow and some digital illiteracy. With a clear vision and defined change management, MGH will be able to drive change through digital transformation effectively and sustainably.
Communication Plan
The executive leadership and MGH board communication plan will focus on the strategic, clinical, and regulatory need to incorporate AI-based predictive analytics into the current EHR infrastructure of the hospital. Special consideration must be given to Leapfrog’s reported postoperative sepsis rate of 4.69, adverse event score of 1.02, and fall rate of 0.199, which are indicators that are identified as urgent threats to patient safety and hospital performance ratings (LeapFrog, n.d.). The leadership should know that the indicators do not only represent clinical gaps but also the risk of reputational damage and financial fines as a result of low-quality outcomes and readmission rates.
The business case needs to show the payback in terms of fewer complications, fewer readmissions, higher patient satisfaction and streamlined clinical processes. In addition, projections for real-time blocks, automation of notifications, and improved care coordination provide a moderate potential non-zero-sum means for achieving the highest possible Leapfrog and Medicare Compare ratings: Dixon et al (2024).
The reason for the change must correspond to the national safety and quality standards, illness encyclopaedias (HIPAA compliance) and scientifically documented scenarios, according to which it has been shown that AI-based early warning systems are able to reduce the death toll of septicaemia.
Workflow Analysis
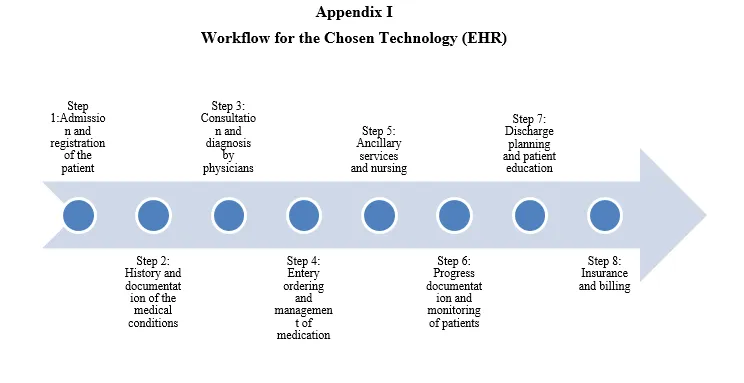
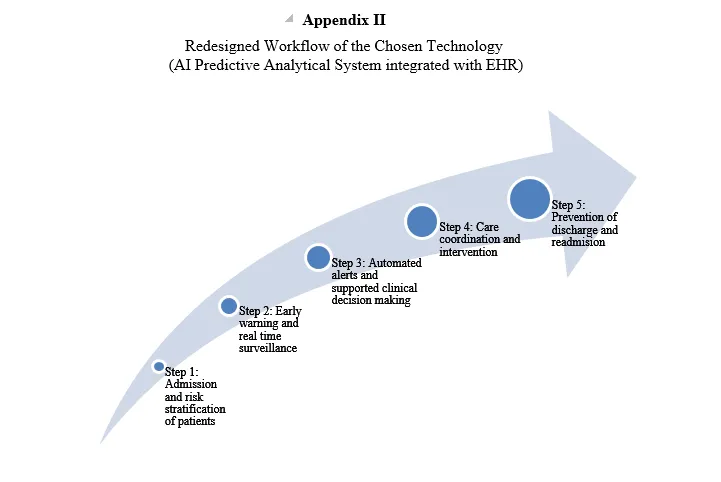
The overall workflow analysis describes the pre- and post-implementation effects of the AI integration on the critical care delivery processes within the MGH organization. The workflows related to pre-implementation include manual risk evaluation, slow sepsis identification, ineffective paper-based checklists, and disjointed interdepartmental communication. Clinicians are now making many decisions based on retrospective data, and alerts are not always directly targeted to the patient or individual trends.
The proposed AI-enabled workflow will include real-time monitoring through wearable sensors, sepsis and falls predictive alerts, and AI-enabled clinical decision support (CDS) embedded in the EHR technology (Calduch et al. 2021). The system has been designed to facilitate early triage, automatic alerting of rapid response teams, and pre-emptive clinical action. The visual workflow diagrams of the current-state processes are provided in Appendix A, and the visual workflow diagrams of the future-state with predictive analytics integration are provided in Appendix B. The representations are a great way to understand how efficiency is enhanced, errors are reduced, and communication flows are improved.
Process Inefficiencies and Value-Added Analysis
The deficiencies in the existing workflow occur mostly at MGH during risk identification, communication handoffs, and interdepartmental care coordination. “The inability to communicate across the various systems and the closed data sharing between each silo is responsible for miscommunication and incident response delays” (Walker and Rahaeyede et al., 2023). Handwriting of vital signs, repetitive checking procedures, and the delay in accessing lab results are non-value-added activities that slow down the timely intervention.
According to the proposed plan, the value-added items are warning patients in real-time about the risk, CDS that prompts with each physician’s rounds, and easy documentation (Sheer et al., 2022). The automated process eliminates redundancy, manual entry, and guesses, and allows clinicians to be proactive rather than reactive. In this way, the specified solution will lead to patient safety improvement, greater clinician efficiency, and a decision-making and outcome-enhancing data ecosystem.
Summary: Final Recommendations and Conclusions
A predictive analytics system utilizing AI in EHRs, which can be embedded into the MGH organization, represents the quality improvement approach that needs to be implemented. According to the results of Leapfrog and Medicare Compare regarding the existing gaps in performance, such as 4.69 sepsis score and A grade overall safety rating, the necessity of change is obvious.
The recommended system will automate early warning processes and reduce unnecessary damage while complying with the national and regulatory requirements. Therefore, through executive sponsorship, interdisciplinary teamwork, and systematic change management, MGH will reinforce the leadership of high-quality, patient-centered care.
Discover expert guidance for NURS FPX 8022 Assessment 3 at Tutors Academy—start crafting your person-centered scholarly project today!
Appendix I
Appendix II
Related Free Assessments for NURS-FPX8022
Instructions To Write NURS FPX 8022 Assessment 4
If you need guidance to write NURS FPX 8022 Assessment 4 Quality Improvement Project Plan Using Informatics/Technology, contact Tutors Academy. Our expert tutors are ready to help you.
Instruction file for 8022 Assessment 4
Contact us to get the instruction file for this assessment.
Scoring Guide for 8022 Assessment 4
Contact us to get the Scoring file for this assessment.
References For NURS FPX 8022 Assessment 4
Afolalu, O. O., Afolalu, S. A., Afolalu, O. F., & Akpor, O. A. (2024). Internet of Things and Software Applications in Patient Safety Adverse Event Detection and Reporting: A Comprehensive Literature Review. 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1109/seb4sdg60871.2024.10629786
Alami, J., Hammonds, C., Hensien, E., Khraibani, J., Borowitz, S., Hellems, M., & Riggs, S. L. (2022). Usability challenges with electronic health records (EHRs) during prerounding on pediatric inpatients. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association Open, 5(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jamiaopen/ooac018
Alharbi, H. A., Alharbi, K. K., & Hassan, C. A. U. (2023). Enhancing elderly fall detection through IoT-enabled smart flooring and AI for independent living sustainability. Sustainability, 15(22), e15695. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215695
Dixon, D., Sattar, H., Moros, N., Kesireddy, S. R., Ahsan, H., Lakkimsetti, M., Fatima, M., Doshi, D., Sadhu, K., & Hassan, M. J. (2024). Unveiling the influence of AI predictive analytics on patient outcomes: A comprehensive narrative review. Cureus, 16(5), e59954. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.59954
Garcia, R., Barnes, S., Boukidjian, R., Goss, L. K., Spencer, M., Septimus, E. J., Wright, M.-O., Munro, S., Reese, S. M., Fakih, M. G., Edmiston, C. E., & Levesque, M. (2022). Recommendations for Change in Infection Prevention Programs and Practice. American Journal of Infection Control, 50(12), 1281–1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2022.04.007
Hidayati, N. N. (2024). Research Article Trends Globally on Translation: A Bibliometric Analysis with ScienceDirect Database. JETLEE: Journal of English Language Teaching, Linguistics, and Literature, 4(2), 169–189. https://doi.org/10.47766/jetlee.v4i2.2868
Kruse, C. S., Mileski, M., Dray, G., Johnson, Z., Shaw, C., & Shirodkar, H. (2022). Physician burnout and the electronic health record leading up to and during the first year of COVID-19: A systematic review (preprint). Journal of Medical Internet Research, 24(3). https://doi.org/10.2196/36200
Luo, H., Liu, J., Fang, W., Love, P. E. D., Yu, Q., & Lu, Z. (2020). Real-time smart video surveillance to manage safety: A case study of a transport mega-project. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 45, 101100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2020.101100
Medicare Compare. (2024). Find healthcare providers: Compare care near you | Medicare. Medicare.gov. https://www.medicare.gov/care-compare/details/hospital/220071?city=Boston&state=MA&zipcode=
Miles, M. C., Richardson, K. M., Wolfe, R., Hairston, K., Cleveland, M., Kelly, C., Lippert, J., Mastandrea, N., & Pruitt, Z. (2023). Using Kotter’s change management framework to redesign departmental GME recruitment. Journal of Graduate Medical Education, 15(1), 98–104. https://doi.org/10.4300/JGME-D-22-00191.1
Mulac, A., Mathiesen, L., Taxis, K., & Granås, A. G. (2021). Barcode medication administration technology use in hospital practice: A mixed-methods observational study of policy deviations. BioMed Quality & Safety, 30(12), 1021–1030. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2021-013223
Sheer, R., Nair, R., Pasquale, M. K., Evers, T., Cockrell, M., Gay, A., Singh, R., & Schmedt, N. (2022). Predictive risk models to identify patients at high risk for severe clinical outcomes with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. Journal of Primary Care & Community Health, 13. https://doi.org/10.1177/21501319211063726
Sittig, D. F., Flanagan, T., Sengstack, P., Cholankeril, R. T., Ehsan, S., Heidemann, A., Murphy, D. R., Adelman, J. S., & Singh, H. (2025). Revisions to the safety assurance factors for electronic health record resilience (SAFER) guides to update national recommendations for safe use of electronic health records. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 9(1), 3–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocaf018
Walker, D. M., Tarver, W. L., Jonnalagadda, P., Ranbom, L., Ford, E. W., & Rahurkar, S. (2023). Perspectives on challenges and opportunities for interoperability: Findings from key informant interviews with stakeholders in Ohio. Journal of Medical Internet Research Medical Informatics, 11(11), e43848. https://doi.org/10.2196/43848
Best Professors To Choose From For 8022 Class
- Lisa Kreeger, PhD, RN.
- Buddy Wiltcher, EdD, MSN, APRN, FNP-C.
- Jill Aston, DNP, MSN, BSN.
- Erica Alexander, DNP, MSN, BSN.
- Linda Matheson, PhD (part-time/adjunct DNP faculty).
(FAQs) related to NURS FPX 8022 Assessment 4
Question 1: From where can I download a free sample for NURS-FPX 8022 Assessment 4?
Answer 1: You can download a free sample for NURS-FPX 8022 Assessment 4 from the Tutors Academy website.
Question 2: What is NURS-FPX 8022 Assessment 4?
Answer 2: NURS-FPX 8022 Assessment 4 develops a Quality Improvement Project Plan using informatics to improve patient safety.
Do you need a tutor to help with this paper for you with in 24 hours.
- 0% Plagiarised
- 0% AI
- Distinguish grades guarantee
- 24 hour delivery

